Nervous System Anatomy Posters Set of 6
NOTES NOTES ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY osms.it/nervous-system-anatomy-physiology THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Network of brain, spinal cords, nerves Sensory/afferent, integrative, motor/efferent functions Sensory/afferent Receptors monitor external, internal environment Conscious stimuli (e.g. vision, hearing, touch) Unconscious stimuli (e.g. pH, blood pressure) Integrative.

Structure of the Nervous System tutor2u Psychology
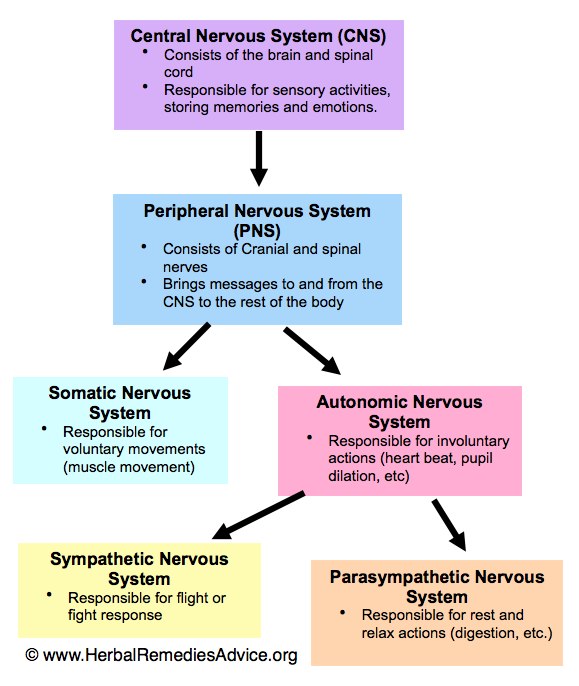
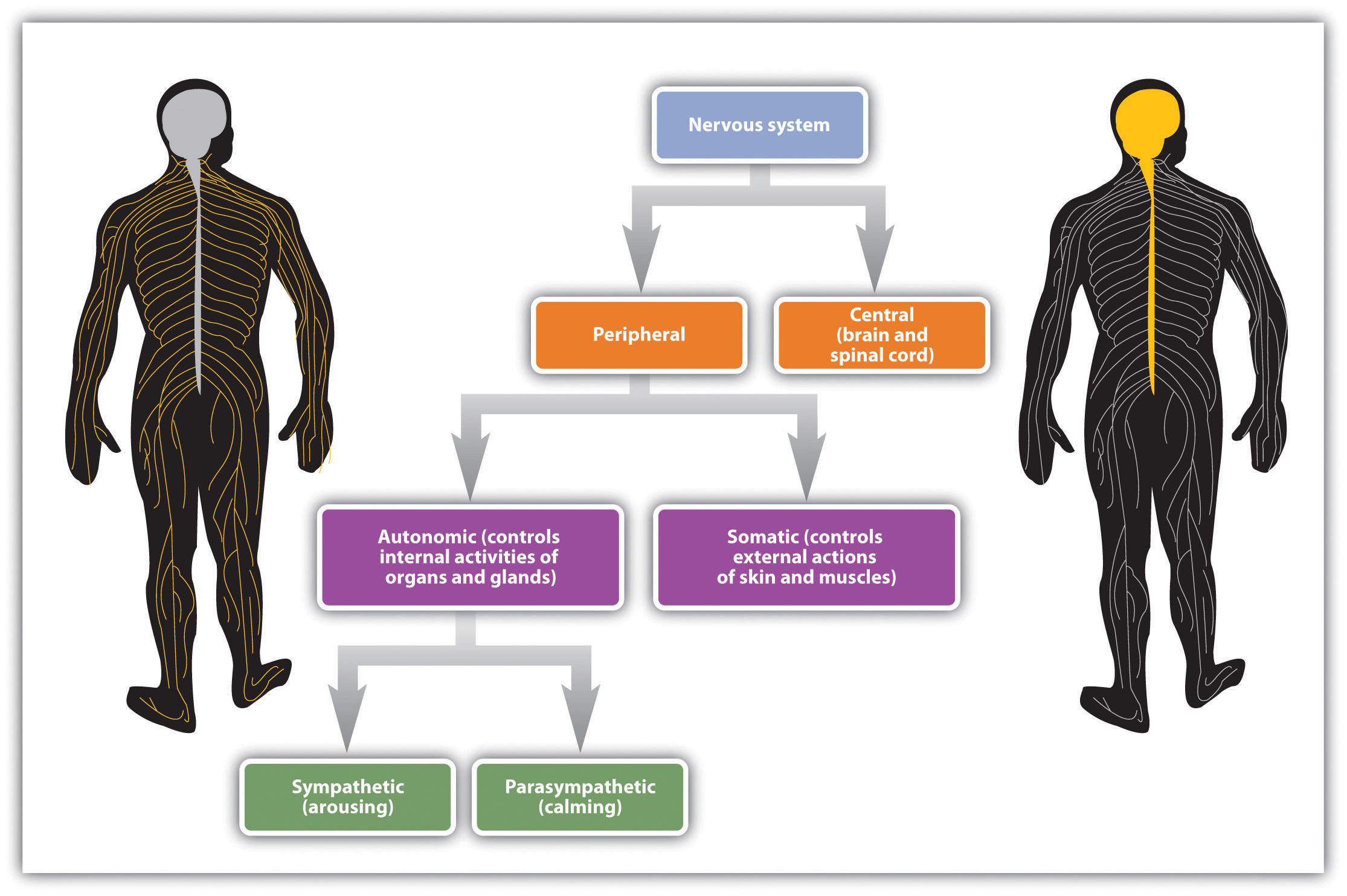
The autonomic nervous system is a component of the peripheral nervous system that regulates involuntary physiologic processes including heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, digestion, and sexual arousal. It contains three anatomically distinct divisions: sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric.

Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology Nervous system, Nclex and Student nurse
Nerves Recommended Video: 3,53,617 What is the Nervous System? The nervous system or the neural system is a complex network of neurons specialized to carry messages. The complexity of the nervous system increases as we move towards higher animals.

About the Nervous System AxoGen, Inc. (AXGN)
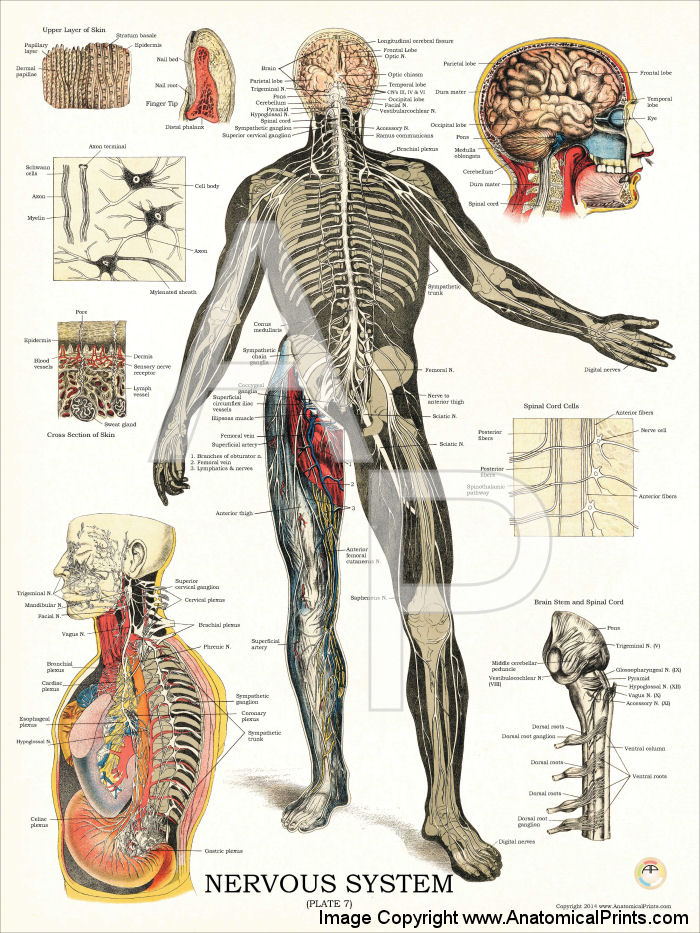
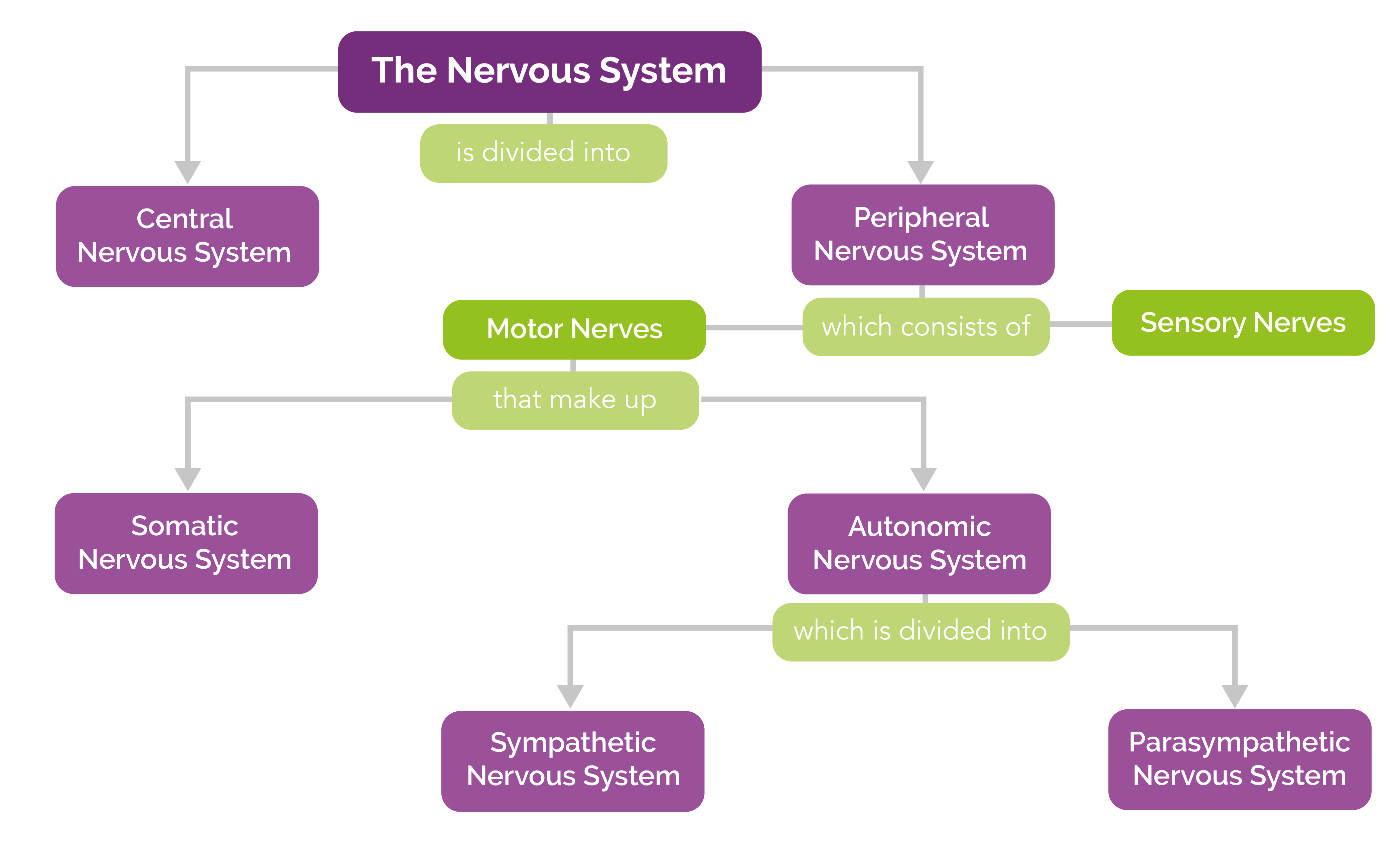
Neuroscience About Parts of the nervous system What are the parts of the nervous system? The nervous system has two main parts: The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and extend to all parts of the body.

BodyPartChart Autonomic Nervous System
The nervous system is a network of neurons whose main feature is to generate, modulate and transmit information between all the different parts of the human body. This property enables many important functions of the nervous system, such as regulation of vital body functions ( heartbeat, breathing, digestion), sensation and body movements.
Nervous System Anatomy Chart 18 x 24
Nervous systems are of two general types, diffuse and centralized. In the diffuse type of system, found in lower invertebrates, there is no brain, and neurons are distributed throughout the organism in a netlike pattern.In the centralized systems of higher invertebrates and vertebrates, a portion of the nervous system has a dominant role in coordinating information and directing responses.
Structure of the Nervous System
Your nervous system's main function is to send messages from various parts of your body to your brain, and from your brain back out to your body to tell your body what to do. These messages regulate your: Thoughts, memory, learning and feelings. Movements (balance and coordination).
5.3 Putting It All Together The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Introduction to
The nervous system is a network of special cells, neurons and ganglia, that work together to carry out the transmission and reception of signals between different parts of our body. The signals are transmitted in the form of electrochemical waves or chemicals.
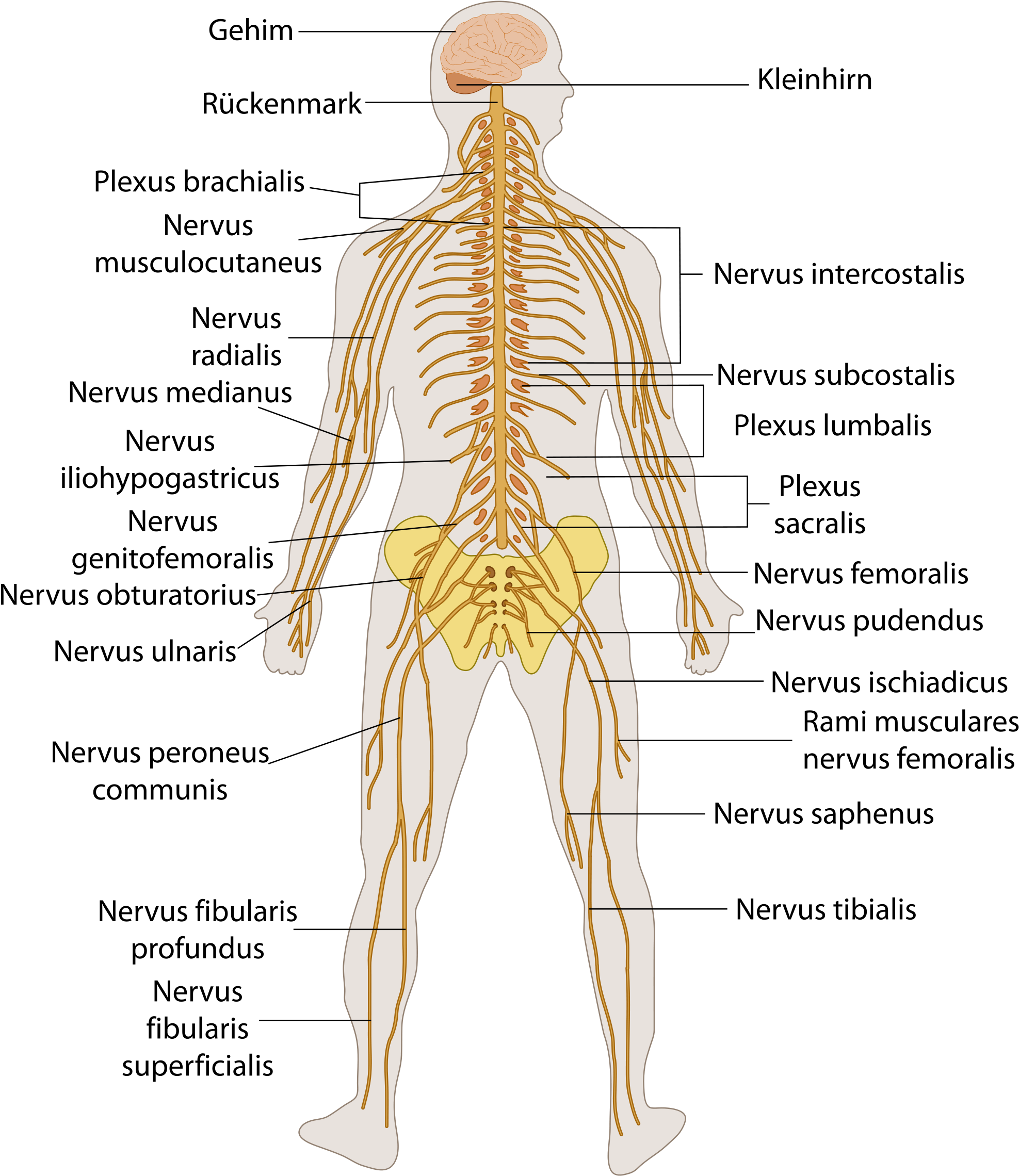
Nervous System Diagram / Nervous System Graph Diagram The central nervous system • the
The nervous system produces a response in effector organs (such as muscles or glands) due to the sensory stimuli. The motor ( efferent) branch of the PNS carries signals away from the CNS to the effector organs. When the effector organ is a skeletal muscle, the neuron carrying the information is called a somatic motor neuron; when the effector.
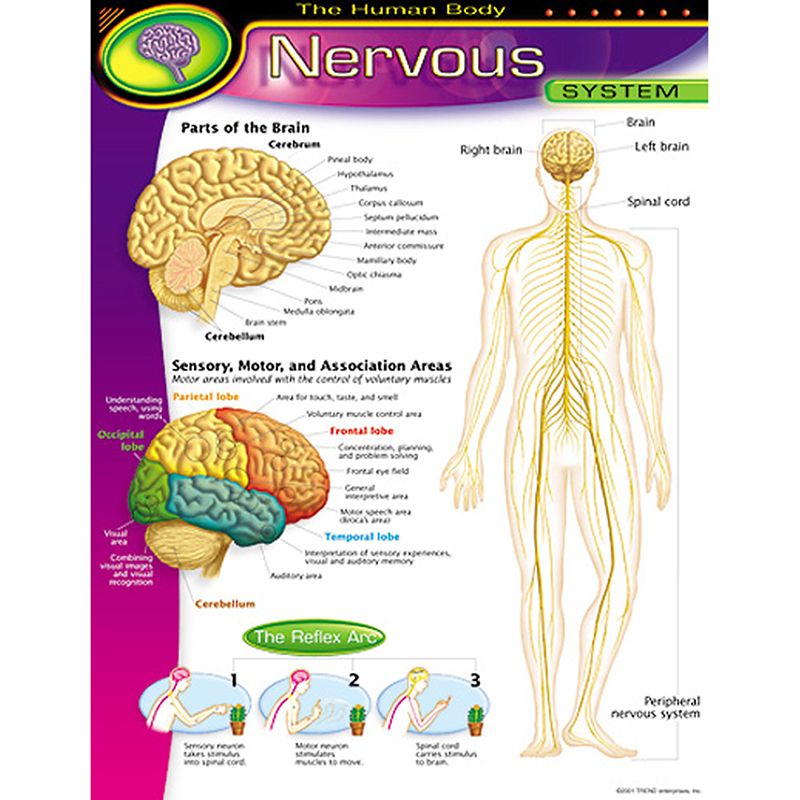
Trend Enterprises, Inc. Chart Nervous System Anatomy Charts Online Teacher Supply Source
The nervous system, essentially the body's electrical wiring, is a complex collection of nerves and specialized cells known as neurons that transmit signals between different parts of the body..
Nervous System Explained Chiropractic Wellness Centre Leicestershire
The central nervous system (CNS) is the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is everything else ( Figure 12.2 ). The brain is contained within the cranial cavity of the skull, and the spinal cord is contained within the vertebral cavity of the vertebral column.
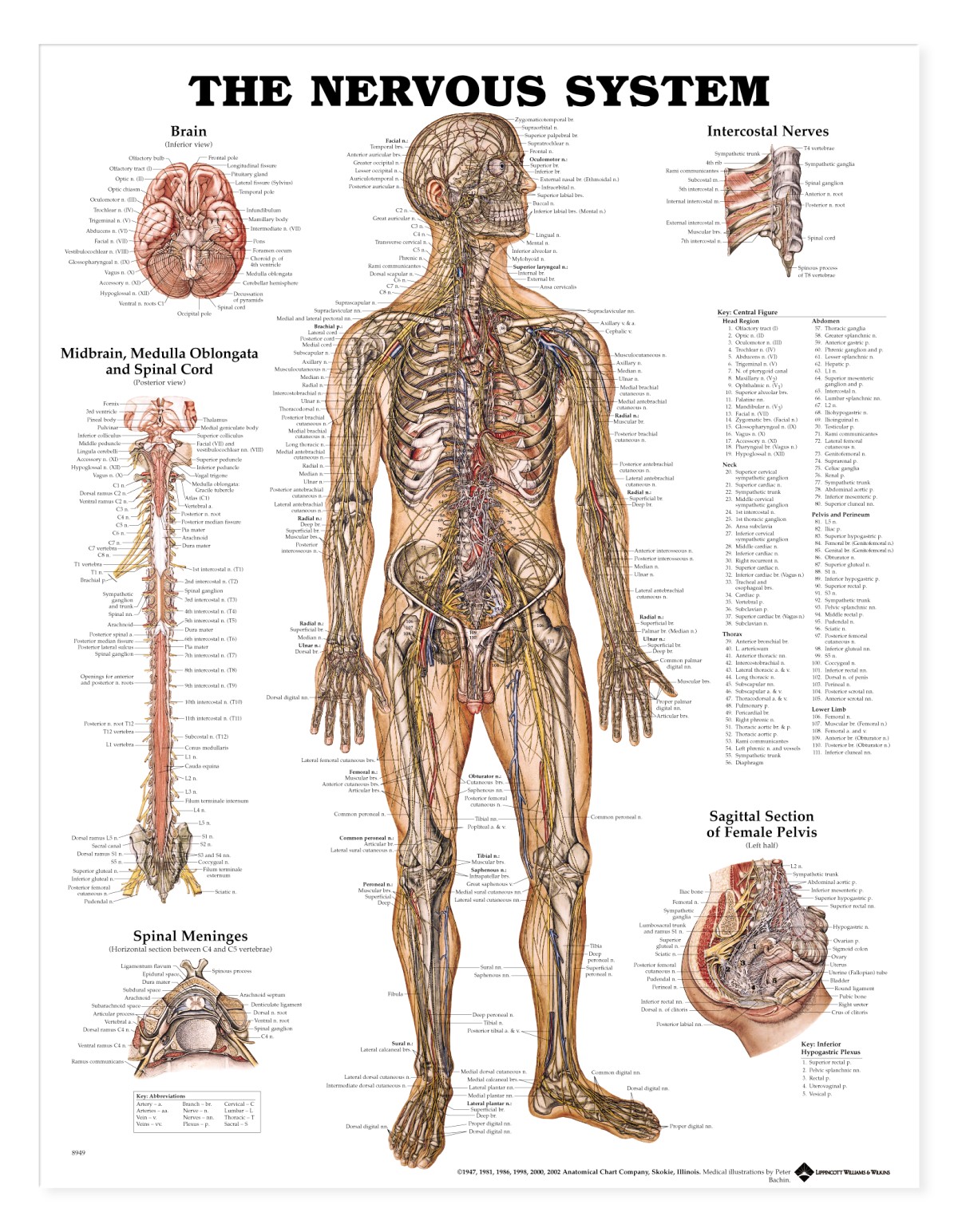
the nervous system diagram labeled
The nervous system has two major parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The central system is the primary command center for the body, and is.

12.1 Structure and Function of the Nervous System Anatomy & Physiology
Lacrimal (eyes), nasopharyngeal (nose) and salivary (mouth) glands: Your autonomic nervous system controls your tear system around your eyes, how your nose runs and when your mouth waters. Skin: Your autonomic nervous system controls your body's ability to sweat. It also controls the muscles that cause hair to stand up.

Nervous system realistic chart Royalty Free Vector Image
Table 11.2.1 11.2. 1: Name of structures depend on the location. A group of neuron cell bodies within the gray matter is called a nucleus in the CNS and a ganglion in the PNS. A bundle of axon within the white matter is called a tract or column in the CNS, and a nerve or nerve fiber in the PNS. CNS.
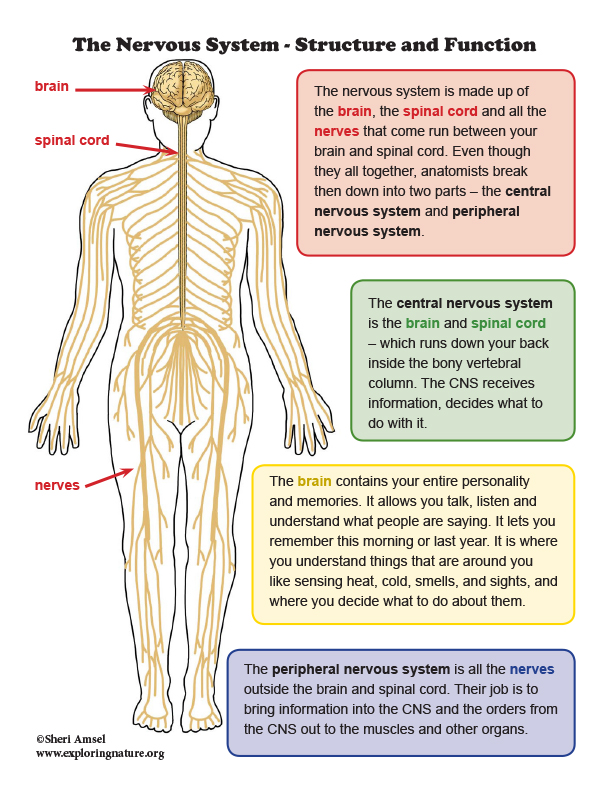
Nervous System Structure and Function MiniPoster
system is the body's prime communication coordination network. It is so vast and complex that, estimate is that all the individual from one body, joined end to reach around the world two and times. The Brain and Spinal Cord are Nervous System. Nerves and Sensory Organs Make Peripheral Nervous System.
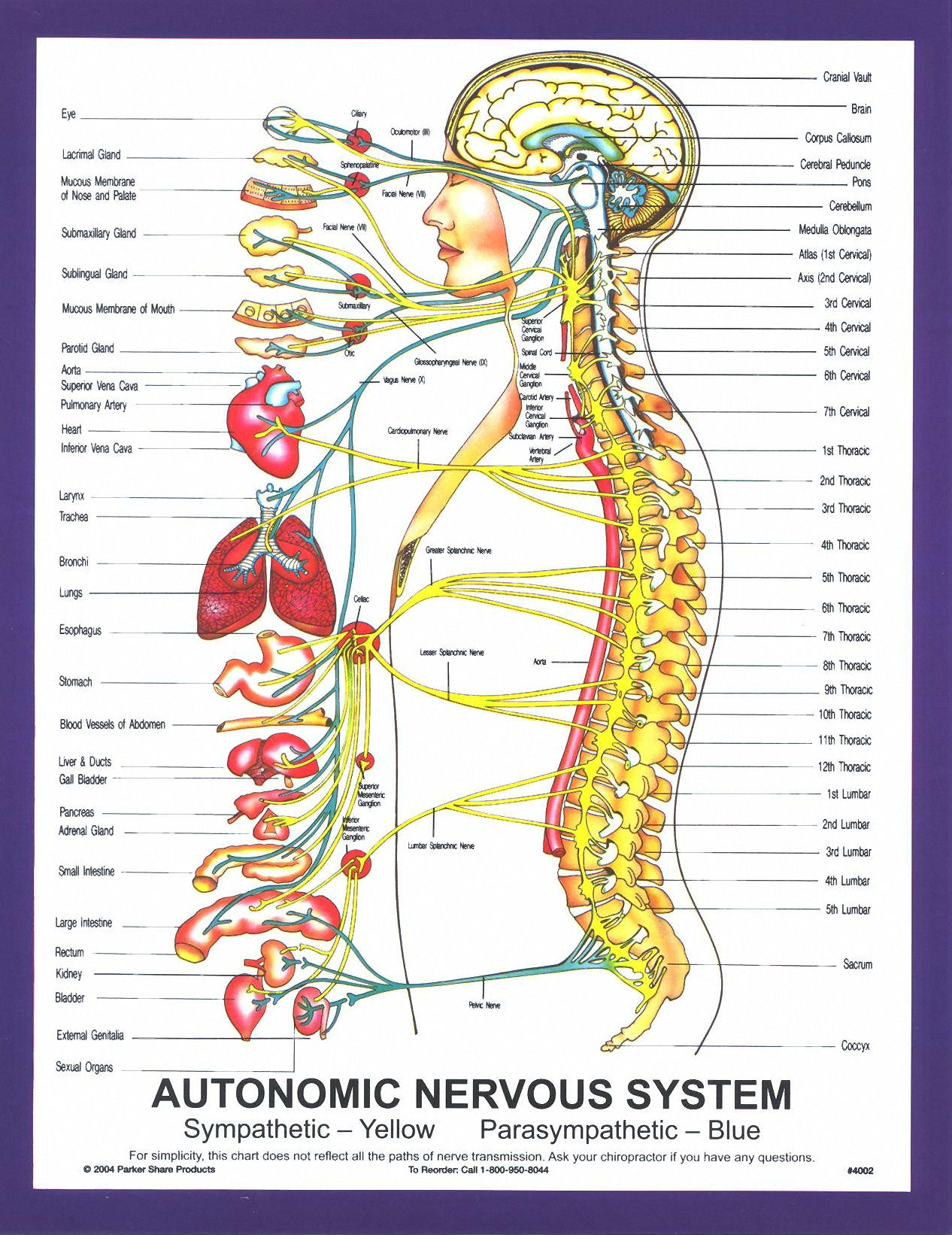
chart_autonomic_nervous_system_large John G. Murray Jr. Chiropractic
Functions of the Nervous System. Transmits information to the processing areas of the brain and spine. Processes the information in the brain and spine - Integration Function. Sends information to the muscles, glands, and organs so they can respond appropriately - Motor Function. It controls and coordinates all essential functions of the.