
Balance KOH + H2SO4 = K2SO4 + H2O (Potassium Hydroxide and Sulfuric Acid) YouTube
Summary A dilute acid has a sour or sharp taste Acids can be harmful and corrosive Common examples: vinegar, lemon juice, car batteries Bases and alkalis

Chemistry Notes Acid, Bases and Indicators Revision Notes & Tests
In this video we'll balance the equation KOH + H2SO4 = K2SO4 + H2O and provide the correct coefficients for each compound. To balance KOH + H2SO4 = K2SO4 +.
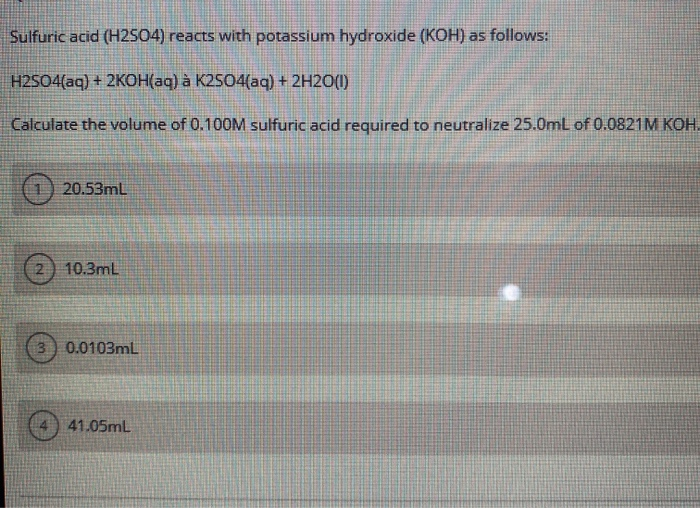
Solved Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) reacts with potassium hydroxide
The reaction of sulfuric acid and potassium hydroxide produces an exothermic reaction, meaning it releases heat. When these two chemicals are mixed, the reaction forms a salt and water. The water created in this reaction can be either an acid or a base, depending on the concentration of the reactants. The heat of formation of potassium sulfate.

Potassium Hydroxide & Sulfuric Acid
Contact Like Us Sulfuric acid (H reacts with Potassium hydroxide (KOH) gives potassium sulfate (K) and water (H O) as products. Heat is released due to neutralization of a strong acid (H ) and a strong base (KOH). In this tutorial, we will discuss followings.
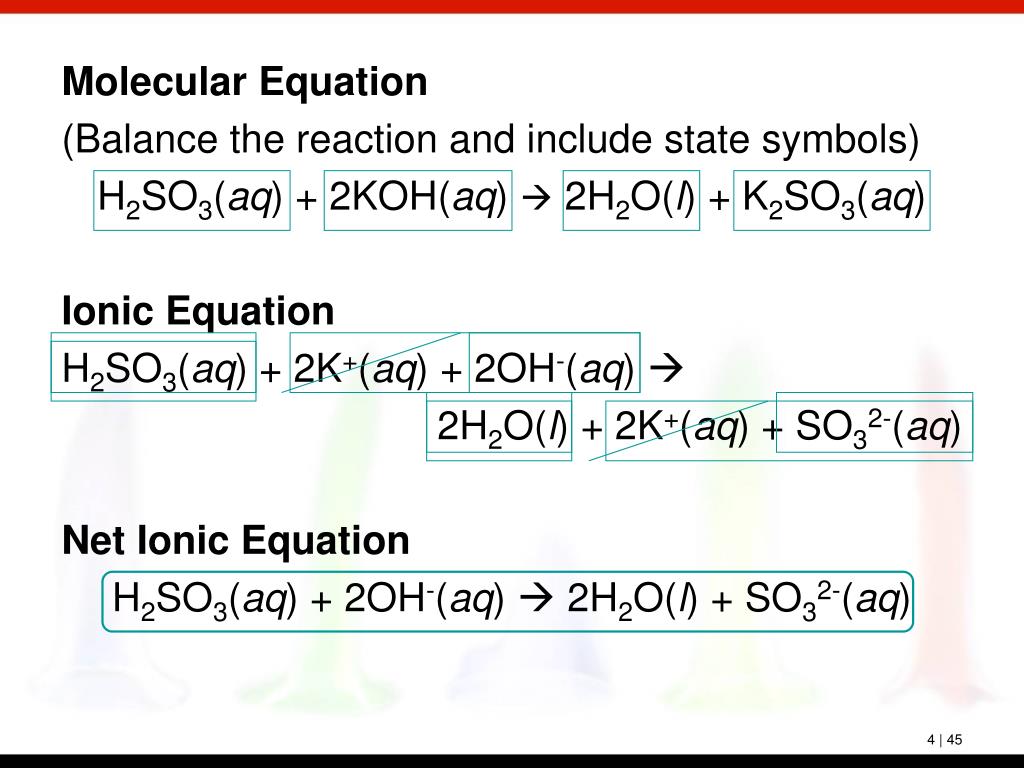
PPT Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5741189
Step-1:write the reaction. H₂SO₄ +KOH ----->K₂SO₄ +H₂O Step-2:In the left side, we have H SO₄ K O To balance this reaction means we need to equalize the number of these above atoms and polyatomic ion from both sides.

Solved Question 18 Sulfuric acid reacts with potassium
Word Equation. Potassium Sulfate + Water = Potassium Hydroxide + Sulfuric Acid. K2SO4 + H2O = KOH + H2SO4 is a Double Displacement (Metathesis) reaction where one mole of aqueous Potassium Sulfate [K 2 SO 4] and two moles of liquid Water [H 2 O] react to form two moles of aqueous Potassium Hydroxide [KOH] and one mole of aqueous Sulfuric Acid [H 2 SO 4]
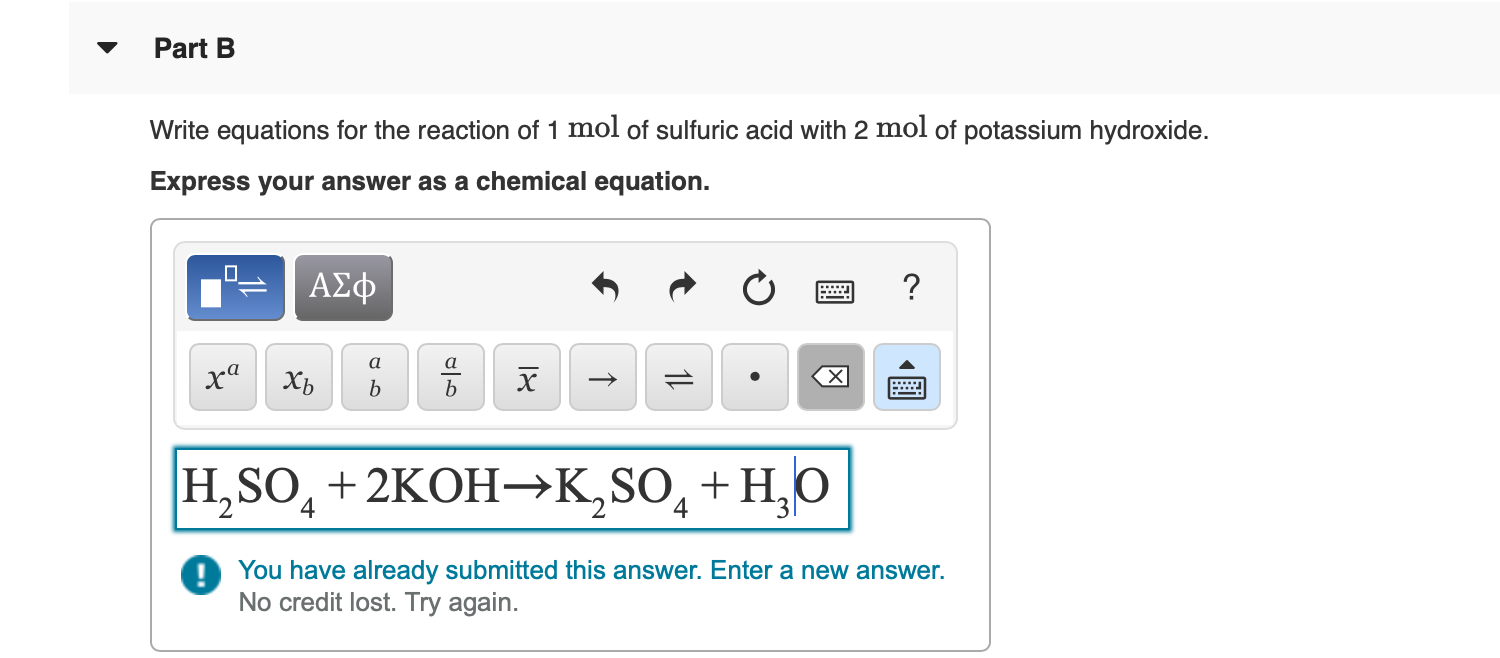
Answered Part B Write equations for the reaction… bartleby
the word equation is: potassium hydroxide + sulfuric acid → potassium sulfate + water; Key fact. Chemical equations contain an arrow and not an equals sign. The arrow means 'reacts to make'.

PPT Reactions in Aqueous Solutions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID519535
The concentration of this acid is known with greater accuracy. The data from this titration is then used to calculate a more accurate value for the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution. A commonly used primary standard for titration with sodium hydroxide solution is the weak acid potassium hydrogen phthalate or KHP (\(\ce{C8H5O4K}\)).
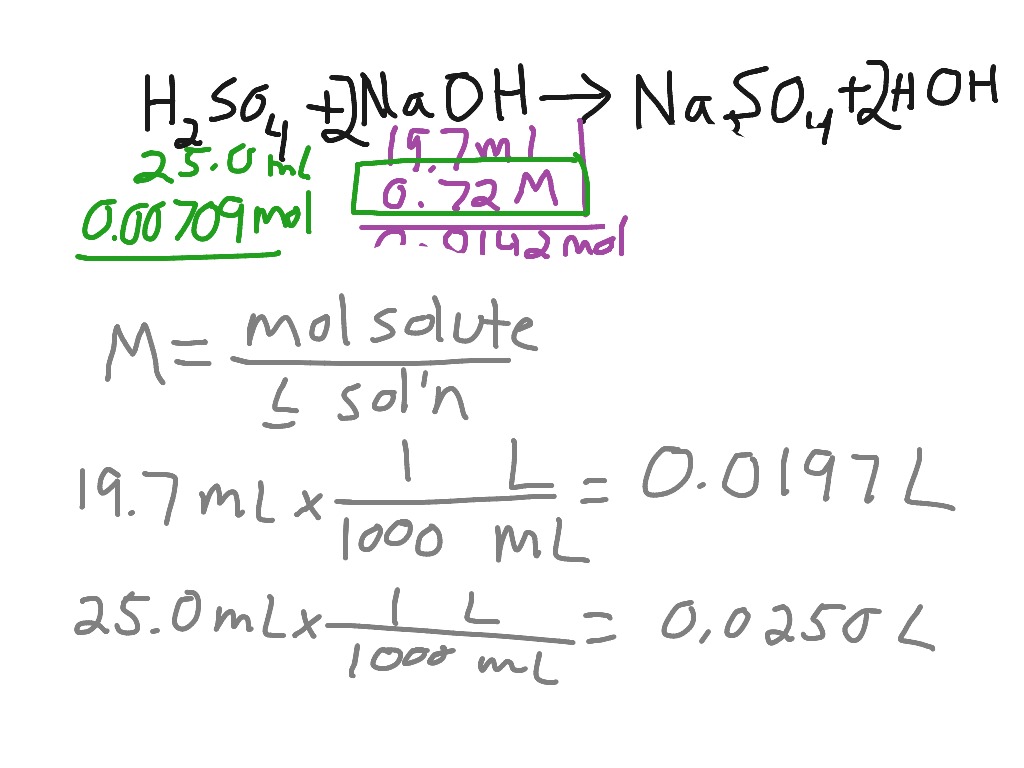
Titration of sulfuric acid with sodium hydroxide Chemistry, Acids and Bases, Stoichiometry
Normality refers to compounds that have multiple chemical functionalities, such as sulfuric acid, H 2 SO 4. A 1 M solution of H 2 SO 4 will contain one mole of H 2 SO 4 in 1 liter of solution,. Why does the calculator use 56.6% weight percentage instead of 28% for ammonium hydroxide? 28% ammonia (NH 3) is equal to approximately 56.6%.

Balance KOH + H2SO4 = K2SO4 + H2O (Potassium Hydroxide and Sulfuric Acid) YouTube
Balanced Chemical Equation H 2 SO 4 + 2 KOH → K 2 SO 4 + 2 H 2 O ⬇ Scroll down to see reaction info and a step-by-step answer, or balance another equation. Reaction Information Word Equation Sulfuric Acid + Potassium Hydroxide = Potassium Sulfate + Water

Potassium Hydroxide and Sulphuric Acid ValentinojoysShannon
The ionization reaction of acetic acid is as follows: CH3CO2H(l) ⇌H2O(l) H+(aq) + CH3CO−2(aq) (4.7.4) Although acetic acid is very soluble in water, almost all of the acetic acid in solution exists in the form of neutral molecules (less than 1% dissociates), as we stated in section 4.1.

Reaction of sulphuric acid and potassium hydroxide Brainly.in
What is the pOH when 5.0 L of a 0.45 M solution of sulfuric acid (H 2 SO 4) is titrated with 2.3 L of a 1.2 M lithium hydroxide (LiOH) solution? SOLUTION. To solve this problem we must first determine the moles of H + ions produced by the strong acid and the moles of OH-ions produced by the strong base, respectively: Acid:

Sulphuric Acid 98, 24 Ton, Liquid, Karan Chemicals ID 22990740773
2. Measure the temperature of the solution. 3. Add an equal volume of 1.0 molar solution of potassium hydroxide and stir. 4. Measure the temperature of the mixture. We have become familiar with acid/base neutralization reactions. The reaction between sulfuric acid and potassium hydroxide leads to the formation of salt and water.

Potassium Hydroxide Sulfuric Acid,hydrochloric acid,nitric acid,hydrogen peroxide,glacial
For graded solutions of potassium hydroxide and of sulphuric acid, data from the International Critical Tables or more recent sources are used as the basis of tables giving the concentrations (wt.%) and densities corresponding to relative humidities in steps of 5 per cent. R.H. Sources of similar data for calcium chloride, sodium hydroxide.
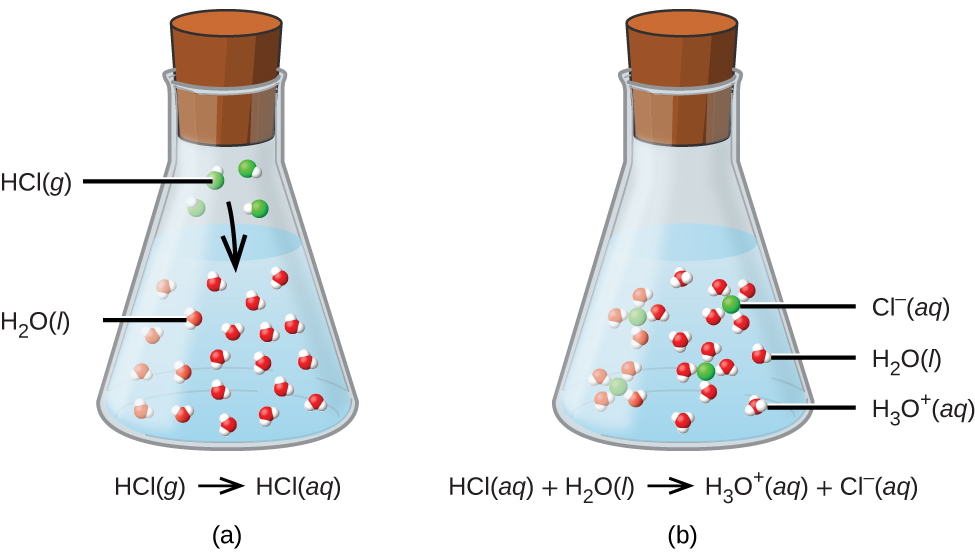
Acids, Bases, Neutralization, and GasForming Reactions (M3Q34) UWMadison Chemistry 103/104
Solubility of Hydrogen in Potassium Hydroxide and Sulfuric Acid. Salting-out and Hydration. P. Ruetschi; and ; R. F. Amlie; Cite this: J. Phys. Chem. 1966, 70, 3, 718-723.. Antisolvent Precipitation of Potassium Bicarbonate from KHCO3 + H2O + Ethanol/2-Propanol Systems in the CO2 Capture Process. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.

Balanced Equation For Sodium Hydroxide And Sulfuric Acid
Balanced Chemical Equation KOH + H 2 SO 4 → KHSO 4 + H 2 O Equation is already balanced. ⬇ Scroll down to see reaction info and a step-by-step answer, or balance another equation. Reaction Information Word Equation Potassium Hydroxide + Sulfuric Acid = Potassium Bisulfate + Water