
parts of a tree and their functions Joan Scales
Each part of a tree crown has a different function. The limbs of the tree extend from the tree trunk, creating structure and attaching branches and stems to the leaves, flowers, and fruits. The limbs also deliver nutrients to various parts of the tree for conversion to energy. The branches and stems of the tree hold the leaves, fruits, and.

FREE Printable Anatomy of a Tree Diagram in 2021 Study printables, Nature study, Tree diagram
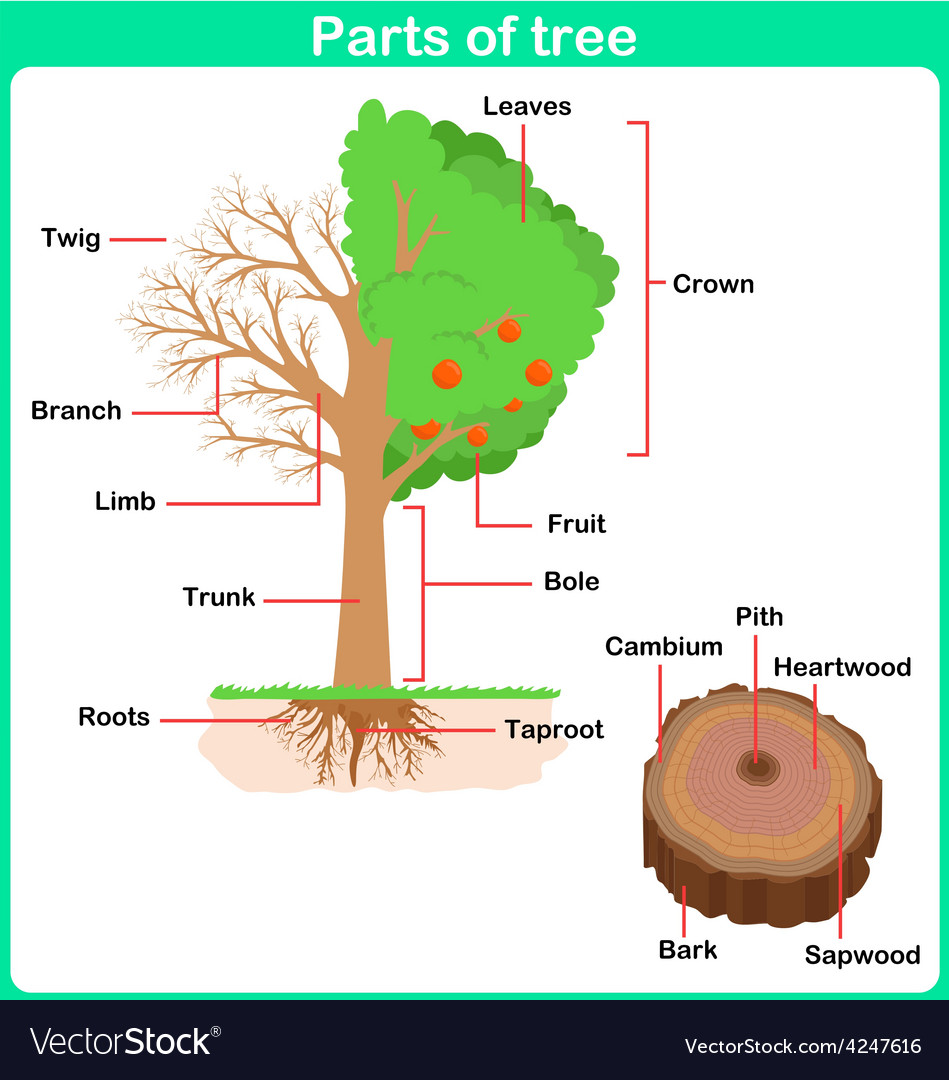
1. Crown. Crown part of the trees | image by Dietmar Rabich via Wikimedia Commons | CC BY-SA 4.0. The top of the tree which contains the most of its leaves and canopy. Most of the photosynthesis of the tree happens here in the crown. The crown of a deciduous tree is usually shaped like an oval or a partial circle.
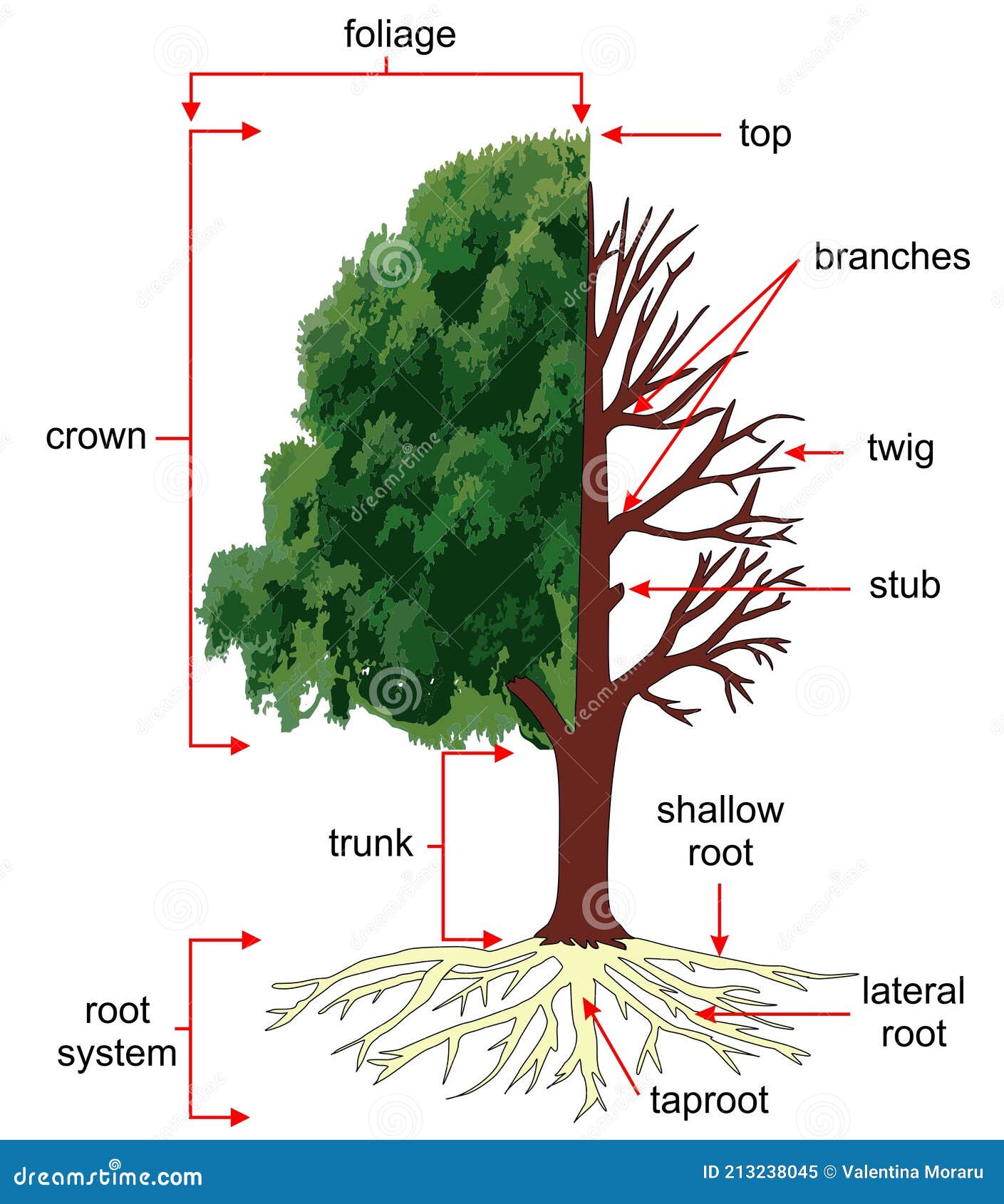
Anatomy of the Tree or Structure of a Tree. Stock Illustration Illustration of root, fruit
Roots. They are the underground extensions of a tree's structure that anchor it in the soil and absorb water and nutrients. They create a network to support the tree's growth and stability. 1. Crown. The crown of a tree is the uppermost part of the tree. It's essentially the "top" or "head" of the tree.

A Guide to Basic Tree Care in Utah Stewart's Lawn
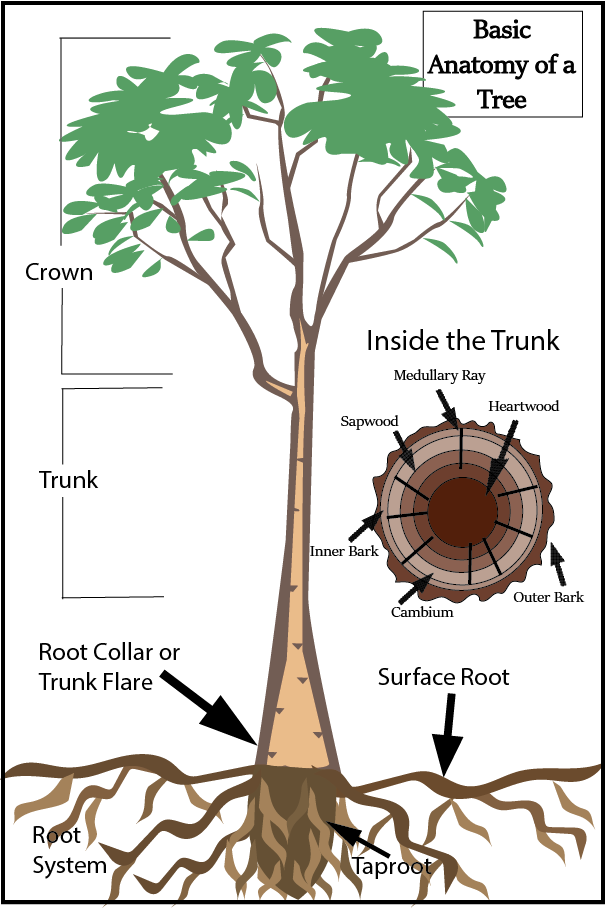
The following are all trunk parts, moving from the outside to the inside. Bark covers the trunk and branches and protects the tree from disease, fire, and injury. Inner bark or phloem carries sap down from the leaves to the branches, trunk and roots. Cambium is a layer that is about two cells thick. Each year it grows new phloem to the outside.
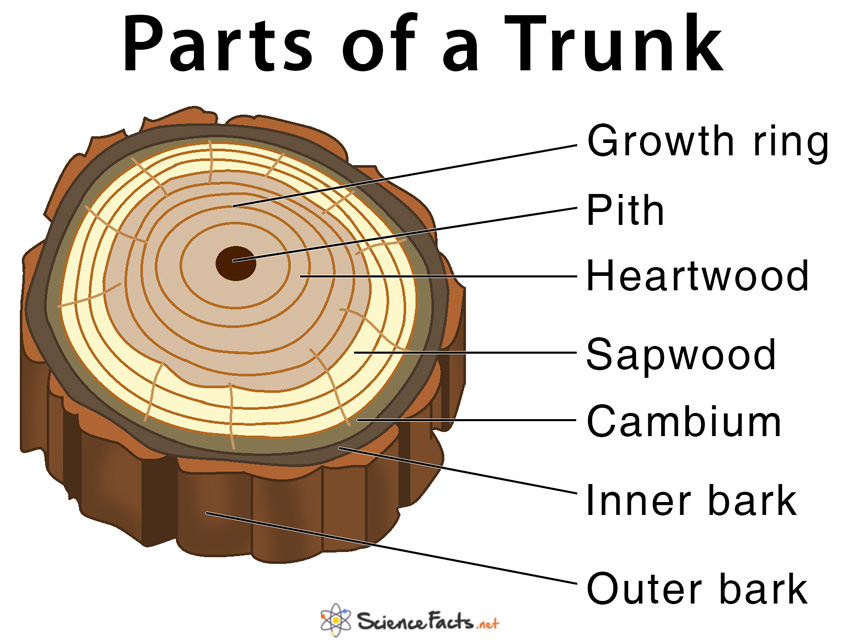
Parts of a Tree and Their Functions Science Facts
Tree - Structure, Growth, Adaptation: Generations of terrestrial plants recycling nutrients and energy into the stratum led to the contribution of developing rich organic soil suitable for large shrubs and herbs. Trees are organized into three major organs: roots, stems, and leaves. All the tree branches and central stem terminate in growing points called shoot apical meristems.

parts of tree English For Life
This is where the tree combines energy from sunlight, carbon dioxide from the air, and water to form sugars and oxygen. This process is called photosynthesis. Leaves and needles also filter the air of particles and create oxygen. Humans and animals exhale carbon dioxide and inhale oxygen. In the height of the summer, leaves are as important to.
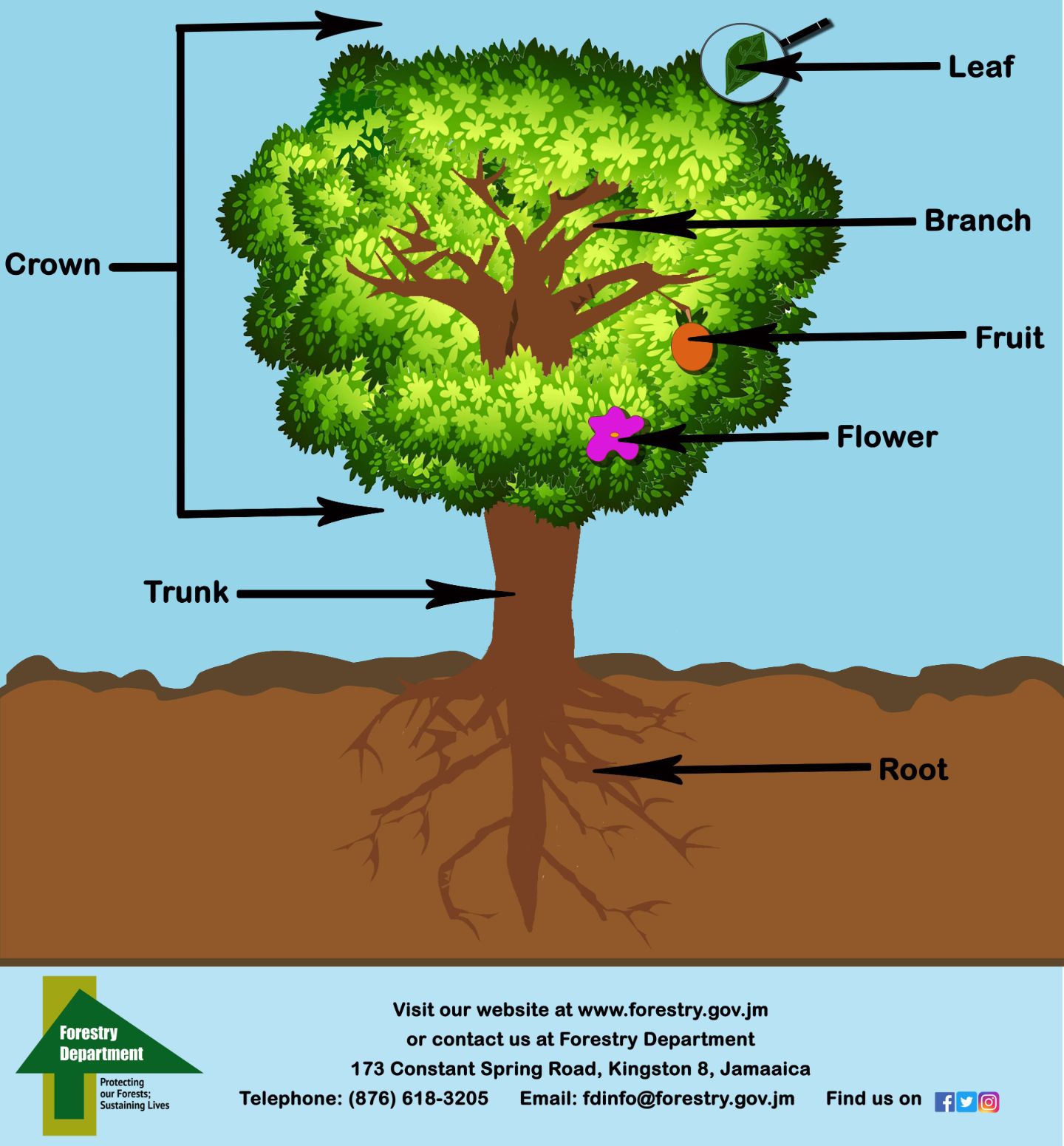
ForestryDepartment Early Childhood
FINDING YOUR PARTS IS AS EASY AS 1, 2, 3! Easy-to-use diagrams of your model help you find the parts you need fast! Or Contact us and we'll help you! With over 60,000 parts in stock in our 40,000 square foot warehouse, consider us YOUR virtual parts room! We ship 80% of orders within one business day, so you get parts FAST!

Parts of a Tree Ellii (formerly ESL Library)
Crown. Above the trunk is the crown. The crown is all the branches and leaves on the tree. The crown is the powerhouse of the tree. The leaves take in sunlight which reacts with the green chlorophyll to transform light into sugars. The process is called photosynthesis and the byproduct is oxygen released into the air.
Leaning parts of tree for kids worksheet Vector Image
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that represents evolutionary relationships among organisms. Phylogenetic trees are hypotheses, not definitive facts. The pattern of branching in a phylogenetic tree reflects how species or other groups evolved from a series of common ancestors. In trees, two species are more related if they have a more recent.

Resources to learn English Trees
324,316 tree parts stock photos, 3D objects, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See tree parts stock video clips. Parts of plant. Morphology of peach tree with fruits, flowers, green leaves and root system isolated on white background. Environment Earth Day In the hands of trees growing seedlings.
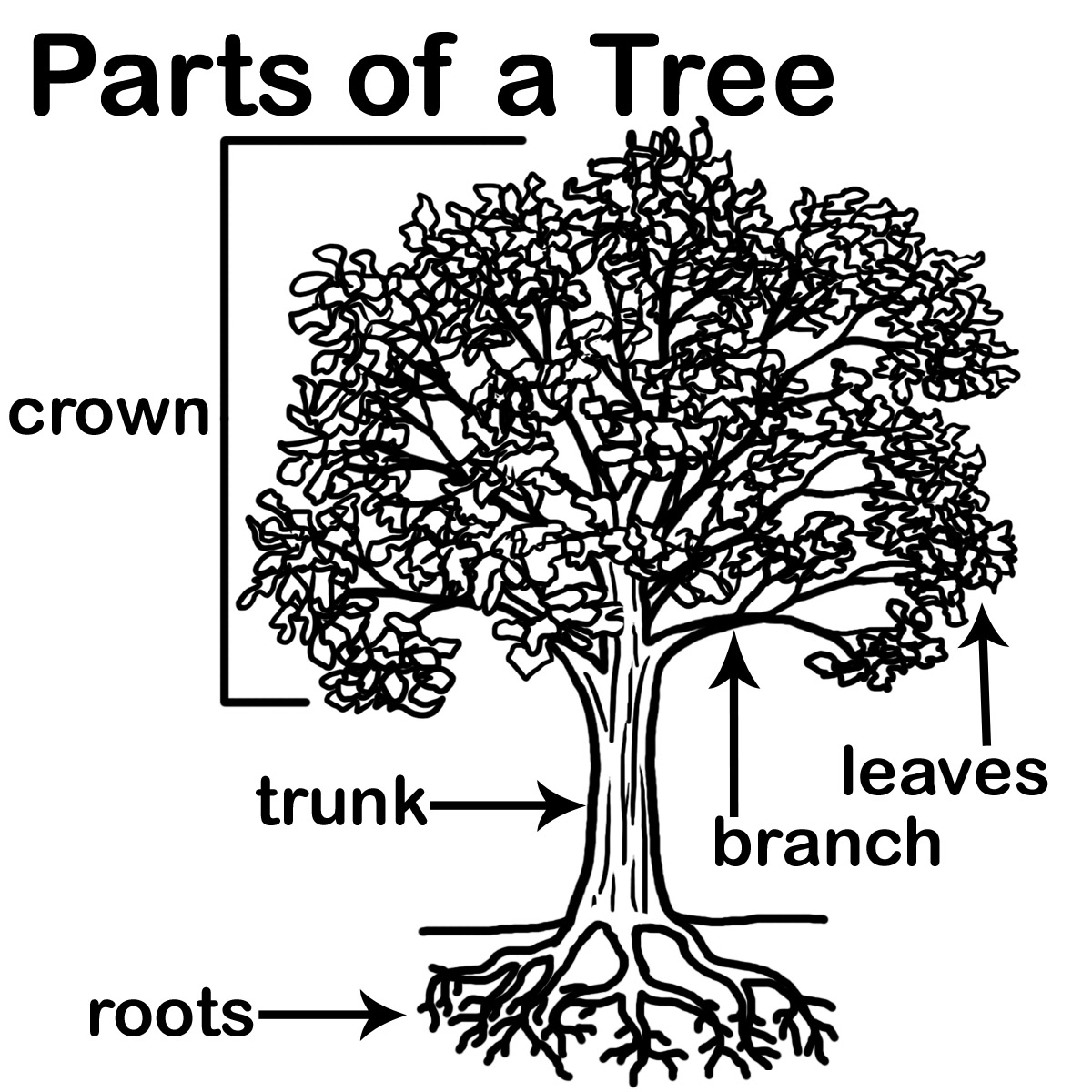
9 Label The Parts Of A Tree Worksheets Kindergarten /
Here are the different tree parts and the functions each one of them serves: 1. Leaves. Leaves belong to the crown of the tree, which is the top part of the tree that grows out of the trunk and includes the branches and stems. While each tree has its unique biological makeup, the average tree consists of 5% leaves.

Parts of a Tree with Roots on a White Background. Stock Vector Illustration of spreading, crop
In short, trees help to maintain the balance of nature. Parts of a Tree Diagram. A mature tree has three basic parts: 1) roots, 2) crown, and 3) trunk or bole. Although the structure of these parts may vary based on the altitude and geographical position of the tree, each of them performs distinct functions.

Parts of the Tree Things from Trees Learn parts of the Tree for kindergarten Kids Entry
There are 6 parts that make up a tree. *See image below: Roots-Secure the tree to the ground. While these parts are underground, they help to collect water and nutrients from the soil to transport up the tree to the other vital parts. Trunk- The main stem of the plant that connects the roots to the limbs (branches) which supports the crown of.
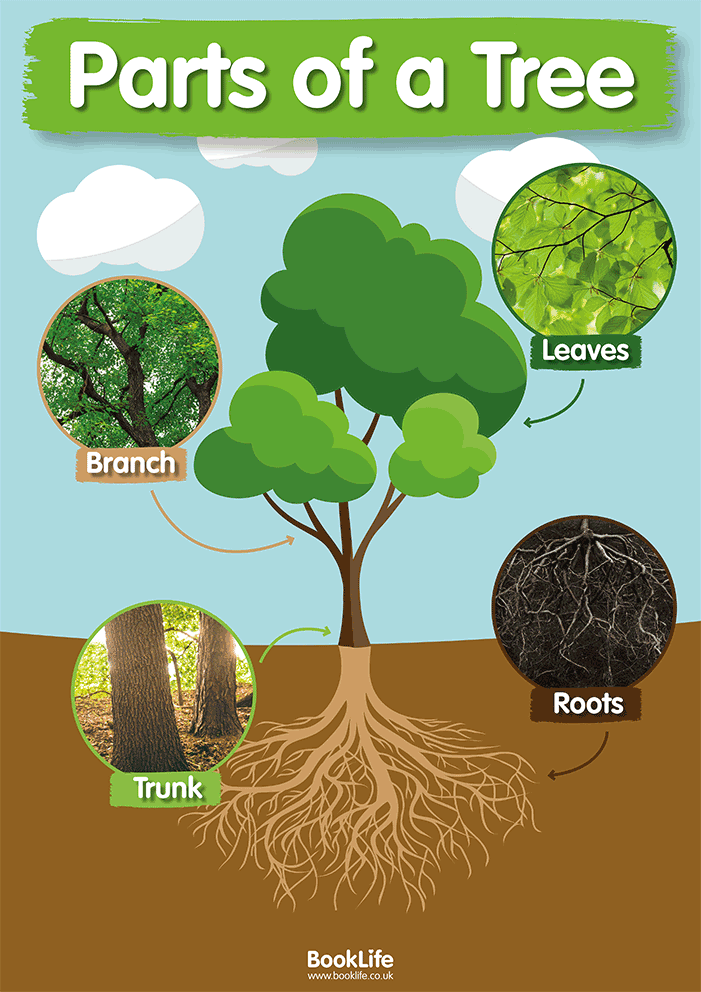
Parts of a Tree Poster BookLife
A tree is a vascular plant of a woody substance that exhibits both primary and secondary growth. The basic sections of a tree are the root system, the trunk, the branches and the foliage. The function and description of each part are detailed below. Vascular plants are plants with tissues that specialize in moving resources through the organism.
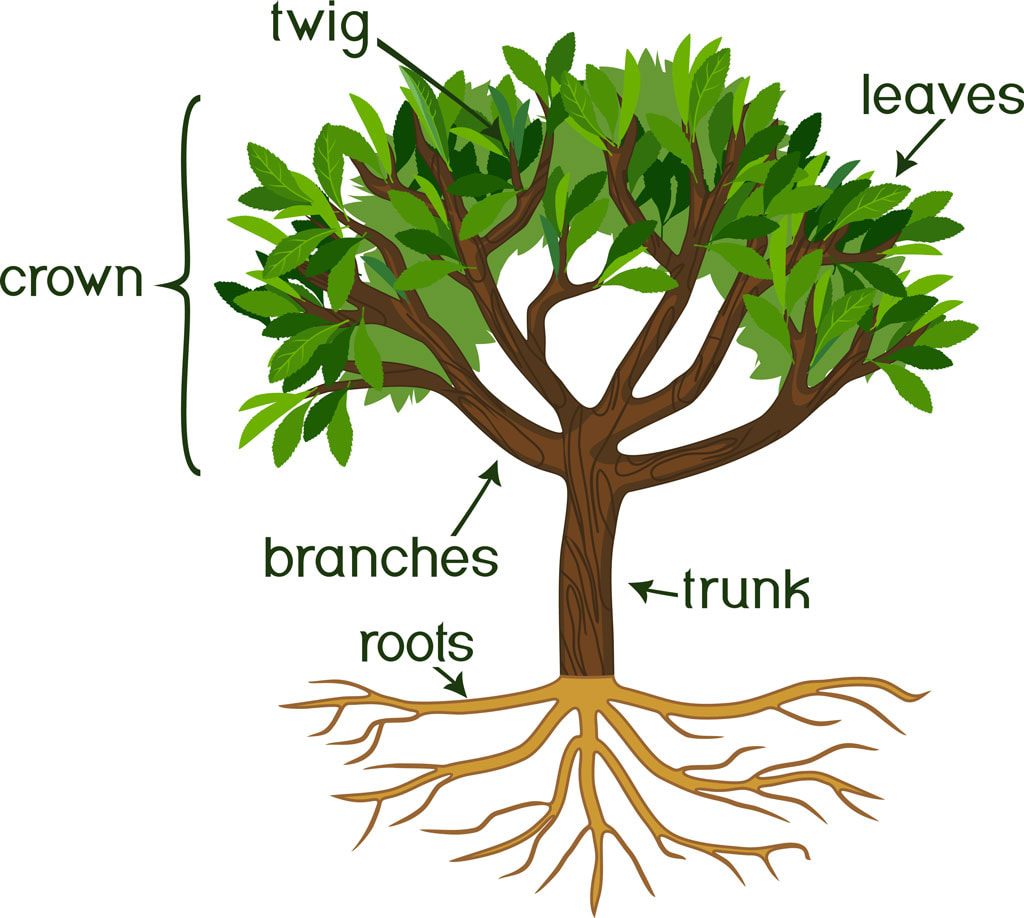
Basic Tree Anatomy The parts of a tree, and their function Snohomish Tree Co.
The trunk is the main structural part of a tree, providing support and stability. It is the vertical, cylindrical section of the tree that extends from the roots to the branches. The trunk is composed of different layers, each with its own unique characteristics and functions. Bark: The outermost layer of the trunk is called the bark.

Parts of a Tree and Their Functions Science Facts
Trees have been on the Earth from around 370 million years. Interestingly, according to a 2015 estimate, the world's tree population is about 3.04 trillion, with 1.39 trillion or 46 per cent in the tropics or subtropics, 0.61 trillion or 20 per cent in temperate zones, and 0.74 trillion or 24 per cent in coniferous boreal forests.