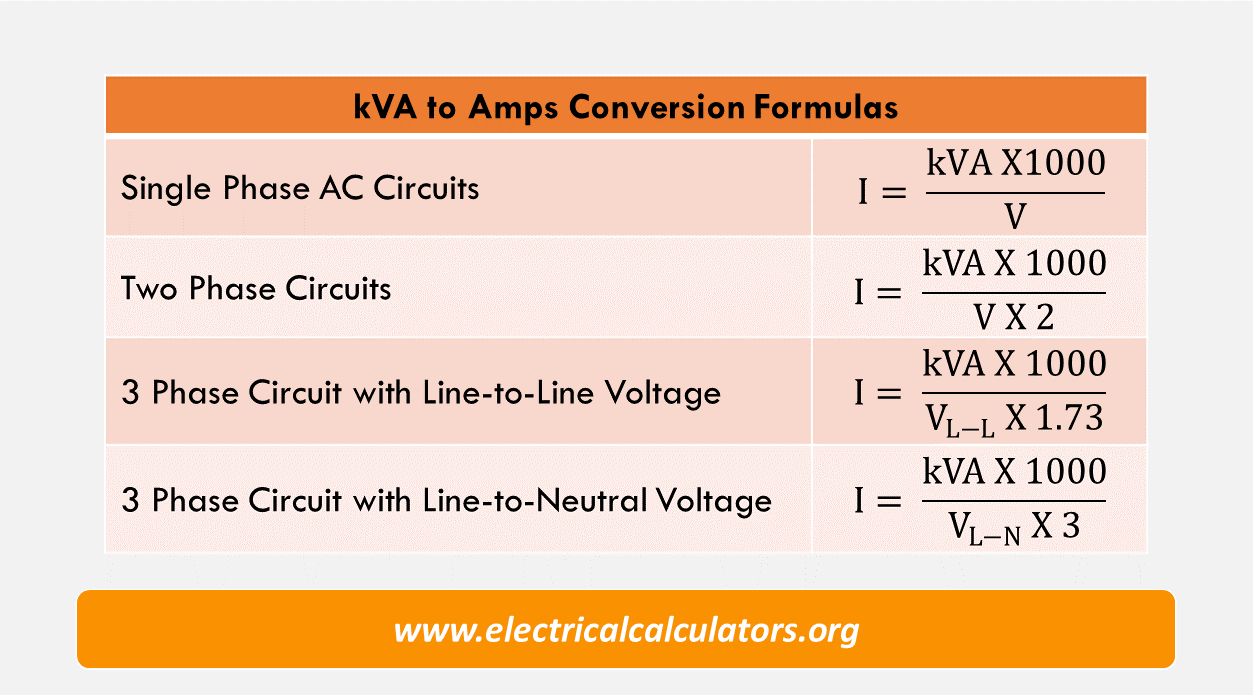
kvatoampsconversionformulas • Electrical Calculators Org
1 kVa to amps (120V) = 8.33 A. 1 kVa to amps (220V) = 4.55 A. 1 kVa to amps (12V) = 83.33 A. Below the calculator, you will find a kVA to amps table (you have to know the voltage - usually 220 V), as well as 2 solved examples of how to convert kVA to amps. You can use it here:

kVA to Amps Conversion Calculator Online Easy Rapid Calcs
First, determine the total current (amps). Next, determine the total voltage (volts). Next, gather the formula from above = kVA = I * V / 1000. Finally, calculate the kVA from Amps. After inserting the variables and calculating the result, check your answer with the calculator above.

KVA TO AMP CONVERSION! AMP TO KVA CONVERSION YouTube
For three phase, kVA can be calculated using the following formula if phase to phase voltage is known. Three phase apparent power, kVA = (3 X Voltage Phase X Current)/1000. Here is an "Amps to kVA converter" that can help you convert amps (amperes) to kVA by simply entering the line voltage and current.
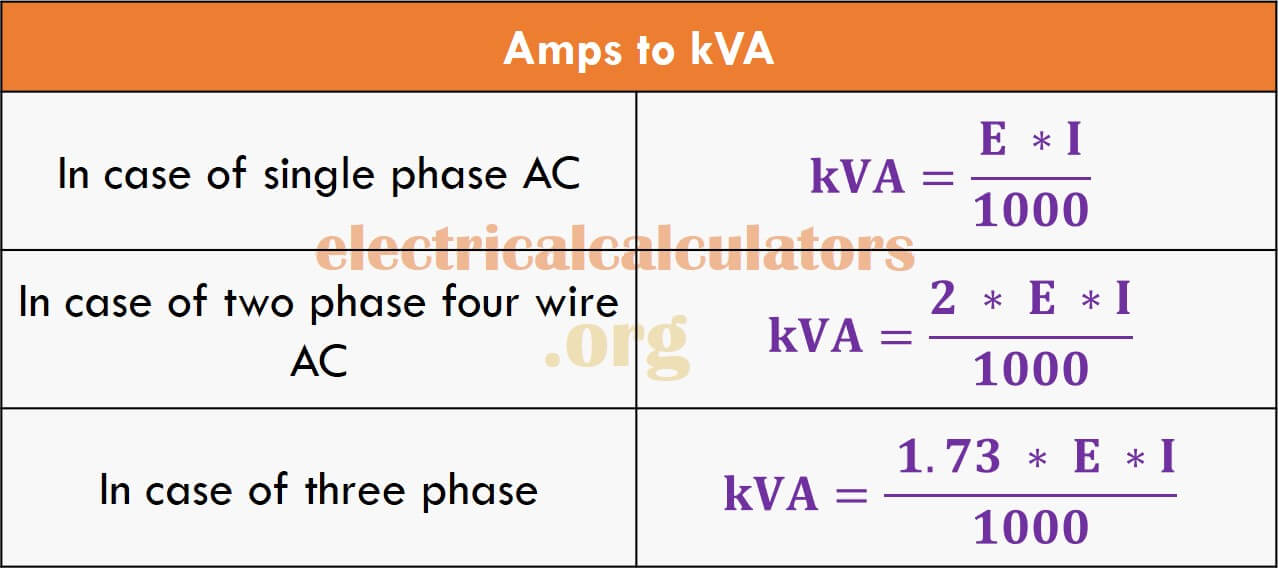
Amps to kVA Conversion Calculator and Formulas [Single, Two, and Three Phase] • Electrical
Amps to kVA Calculator. The following Amps to KVA conversion calculator will convert the current "I" in amperes "A" to apparent power "S" in kVA "kilovolt amperes", VA "volt-amp", mVA "millivolt amps" and MVA "mega volt amp".. To calculate the kVA rating of a machine from the amperage rating, just enter the value of current in amperes, voltage in volts, select power.
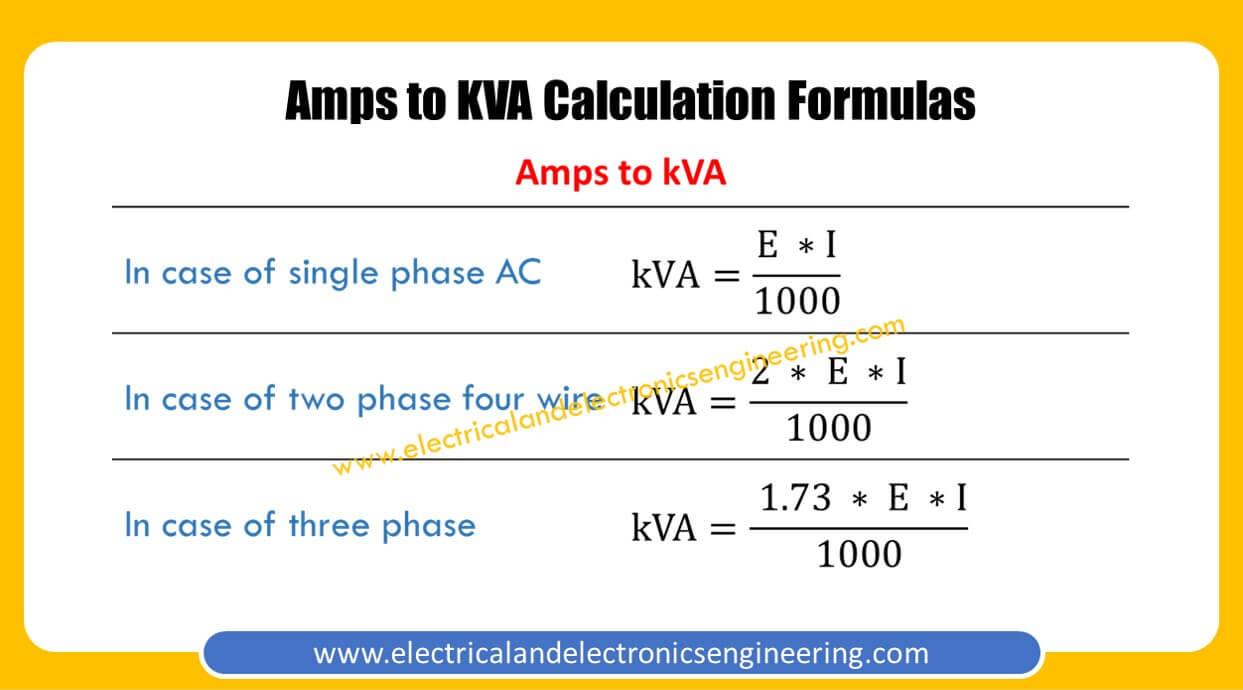
Amps to kVA Conversion Formula Electrical and Electronics Engineering
How to use this Volts and Amps to kVA calculator. What does kVA mean? kVA is an abbreviation for kilovolt-amperes, which is a unit of apparent power. Apparent power is the power that we can potentially draw from an electrical power system. We can determine the amount of apparent power by multiplying together the rated voltage and amperage of.
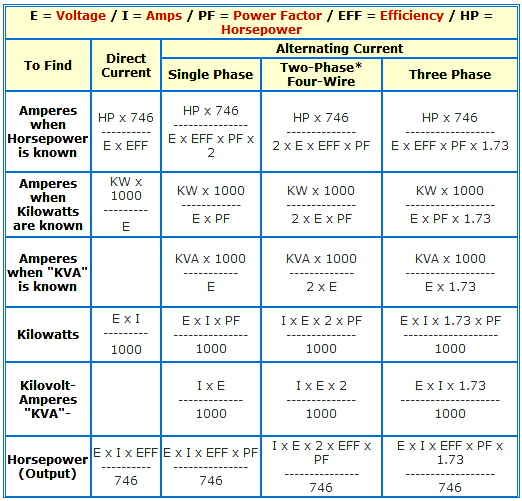
Formula of AMP, KW, KVA, HP for AC and DC Voltages Inst Tools
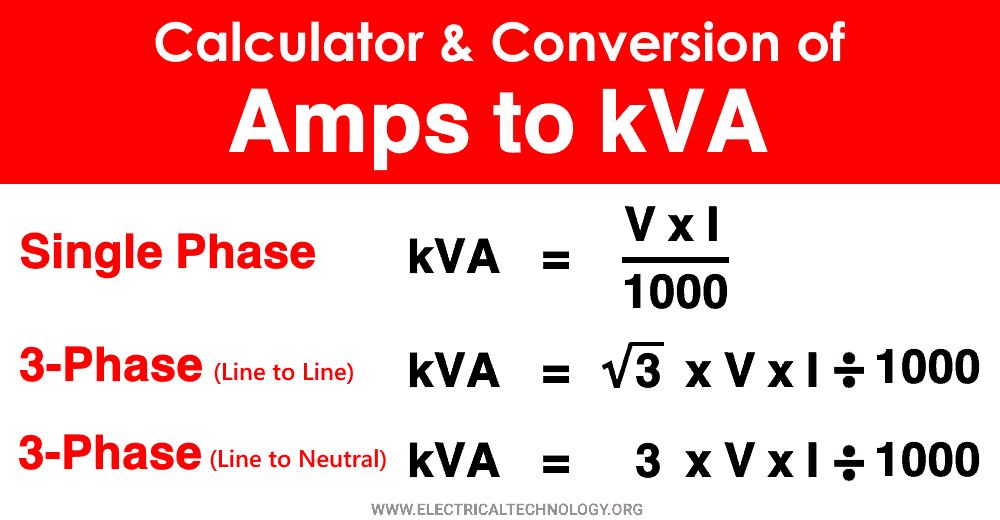
Calculation of Single phase amps to kVA S (kVA) = I (A) x V (V) / 1000, which means that the apparent power in Kilovolt-amps is calculated by multiplying the current in amps with the voltage in volts and dividing the results by 1000. Calculation of three phase amps to kVA Line to Line Voltage

Amp To Kva Calculator Wiringvio
The Amps to kVA Calculator is a tool that helps to convert the current measurement in amps (A) to apparent power measurement in kilovolt-amps (kVA) based on the voltage in volts (V) and the phase of the current. The calculator uses the following formulas: 1-Phase: S (kVA) = I (A) × V (V) / 1000

kVA to Amps Conversion Calculator Online Easy Rapid Calcs
Step 1: Multiply the amps by the voltage indicated in the formula and divide them by 1000. For example, a three-phase fan (3P) has a current of 10 A with a voltage of 208 VL-L, multiply 10 A by the voltage of 208 V , the root of three and divide by 1000, which will result in: 3,6kVA. (10Ax208Vx√3) / 1000 = 3,6kVA).
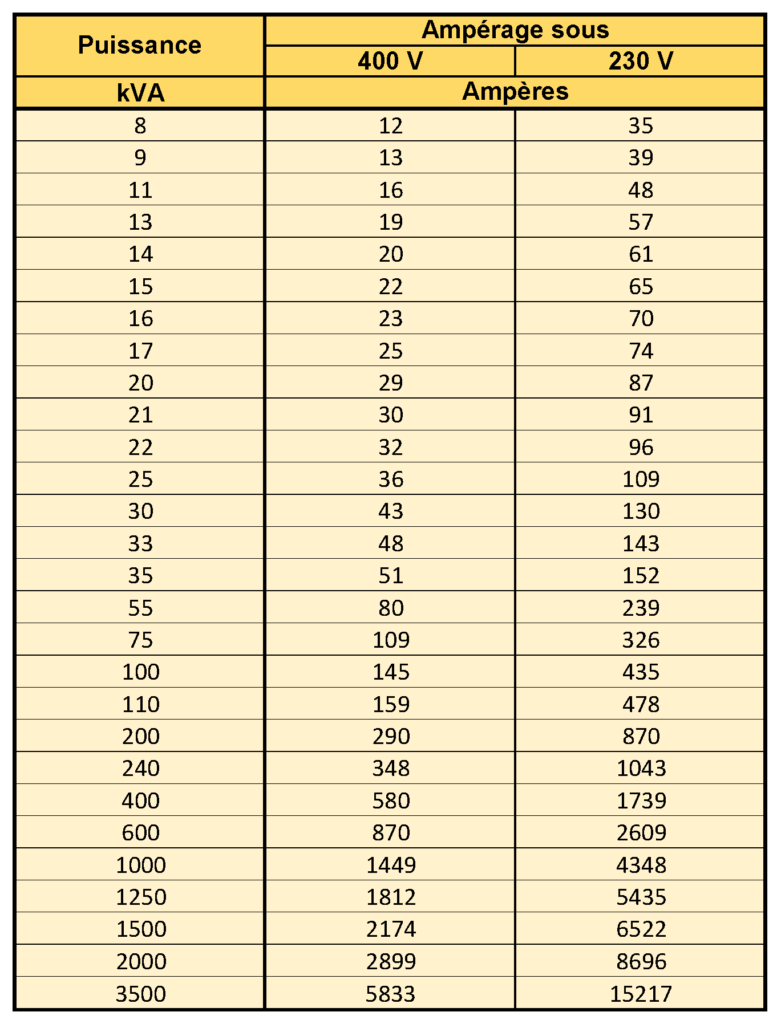
CONVERSION kVA Ampères BD Consult Energie
Home Electrical Calculators Electrical Conversion Amps to Kilovolt-Amps (kVA) Conversion Calculator Convert amps (A) to kilovolt-amps (kVA) to find the power rating of an electrical system by entering the current in amps and voltage below. The calculator supports single-phase and three-phase systems. Phase: Current: amps Voltage: volts

kVA to Amps Calculators, formula, chart, convert and transformer free.
For converting current to apparent power (Amps to kVA), you need to get the following data such as line voltage and nature of the supply. Look at the apparent power formula, S (VA) = I(A) * V(V) For Calculating kVA we need to divide by 1000, Therefore S(kVA) = I(A) × V(V) / 1000

different between single phase kva and 3 phase kva YouTube
Suppose you have an industrial oven with a KVA rating of 150 and a voltage rating of 480 volts. To convert KVA to amperage, you can use the formula: Amps = KVA / (Volts x Power Factor) Amps = 150 / (480 x 0.9) Amps = 347.22. So the industrial oven can draw a maximum of 347.22 amps at 480 volts with a power factor of 0.9.
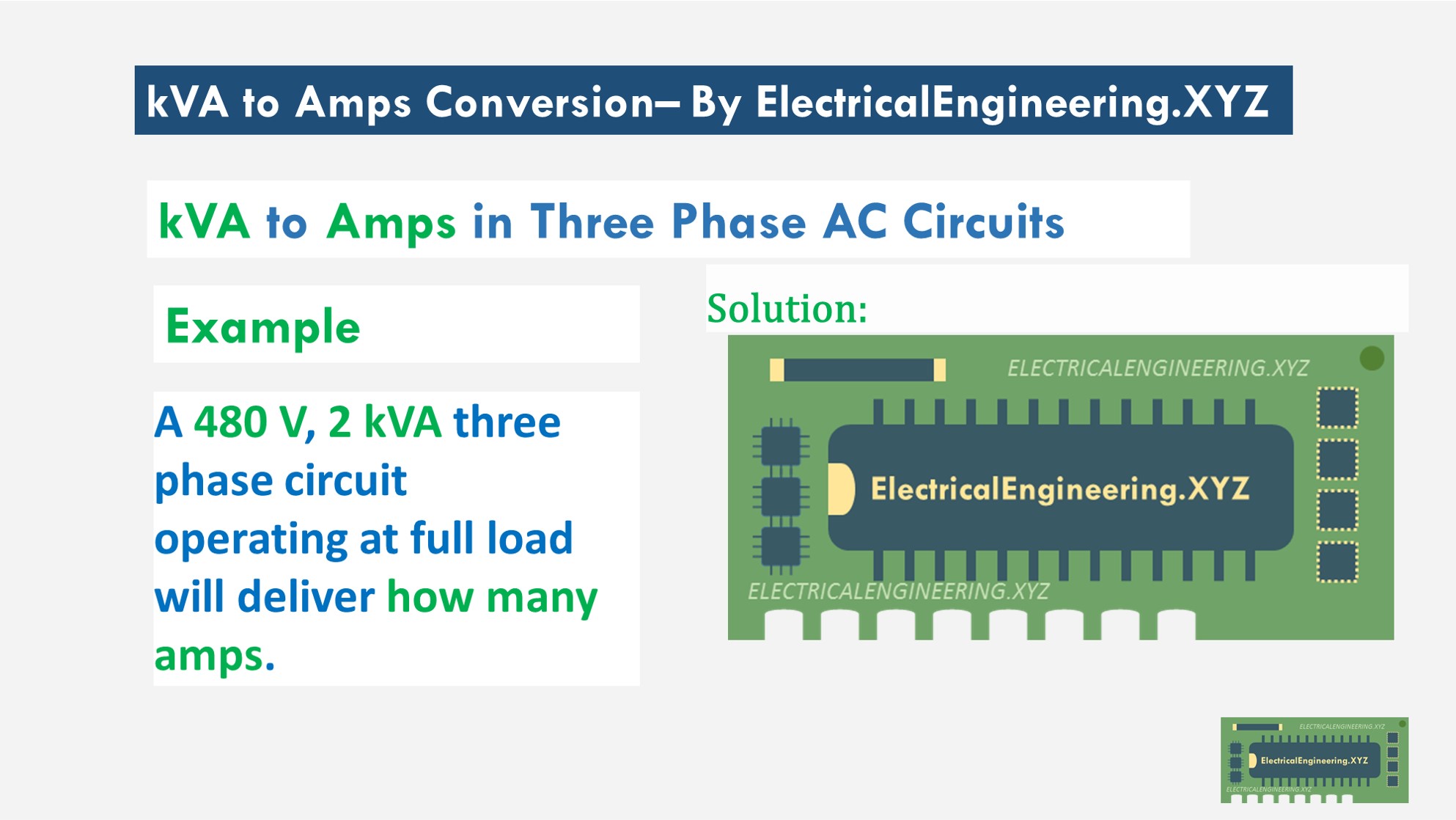
kVA to Amps Conversion Formulas for Single, Two, and Three Phase AC Circuits [Video]
The reactive power Q in volt-amps reactive (VAR) is equal to the voltage V in volts (V) times the current I in amps (A) time the sine of the complex power phase angle ( φ ): Q(VAR) = V(V) × I(A) × sin φ The power factor (FP) is equal to the absolute value of the cosine of the complex power phase angle ( φ ): PF = |cos φ | Energy & power calculator

Conversión de amplificador a kVAcálculos para transformadores y generadores libres. Raumpflege
The formula to convert Amperes (Amps) to Kilovolt-amperes (kVA) is as follows: kVA = (Amps * Volts) / 1000 Where: kVA is the Kilovolt-amperes, Amps is the current in Amperes, and Volts is the voltage in Volts. This formula takes into account the current and voltage and calculates the apparent power in kVA. Example
Calculadora De Amperios A KVA ¿La Forma Correcta De Convertir Amperios A KVA? Electrositio
Multiplication of current (amp) and voltage (volt) makes volt-ampere a unit of power and the equation divides these volt-amperes by 1000 to convert them into kilovolt amperes (kVA). This calculator calculates apparent power units both for single-phase as well as 3 phase voltage.

How to find Amps from KVA ? How to Convert KVA to Amps in Generator Asad Electrical YouTube
This kVA to amperage calculator will help you determine the electric current strength an alternating current system experiences at specific power and voltage loads. With this calculator and by the end of this text, you will be able to: Learn how to convert kVA to amps; Explore the formulas to convert kVA to amps; and

Amps to kVA Calculator & Convert Amps to kVA (A to kVA) Online Electrical4u
Amps to kVA calculator button to get the result in kilovolt-amps (kVA). Single phase Amps to kVA calculation Amps: Voltage: Calculate kVA kVA: S(kVA) = I(A) × V(V) / 1000 The apparent power S in kilovolt-amps (kVA) is equal to the phase current I in amps (A), multiplied by the RMS voltage V in volts (V), divided by 1000.