
Daydreaming shows your smartness, creativity
Maladaptive daydreaming occurs when a person engages in prolonged bouts of daydreaming, often for hours at a time, to cope with a problem. The daydreaming is "maladaptive" because it causes significant distress and impairment. The daydreams are often vivid and complex plots that elicit a great deal of emotion.
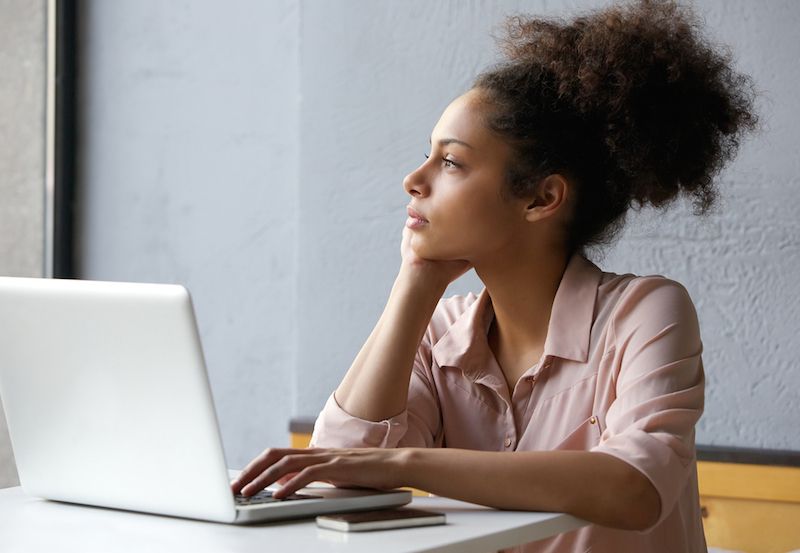

Surprising Facts About Daydreaming Live Science
After a long day at work or after a disagreement with a friend, let your mind float away to something completely unrelated and pleasurable. This might help you forget about and distance yourself from the worrisome circumstances.

You can spend your time daydreaming or make use of it in other ways. Erik… Maladaptive
Daydreaming is a capability supported by our ability to imagine (which some people associate with "right-brain" activities) whereas being logical, verbal, and orderly is supported by our rational.

Maladaptive daydreaming Symptoms and management
During quiet waking, brain activity in mice suggests the animals are daydreaming about a recent image. Having daydreams about a recently viewed image predicted how the brain would respond to the image in the future. The findings provide a clue that daydreams may play a role in brain plasticity.
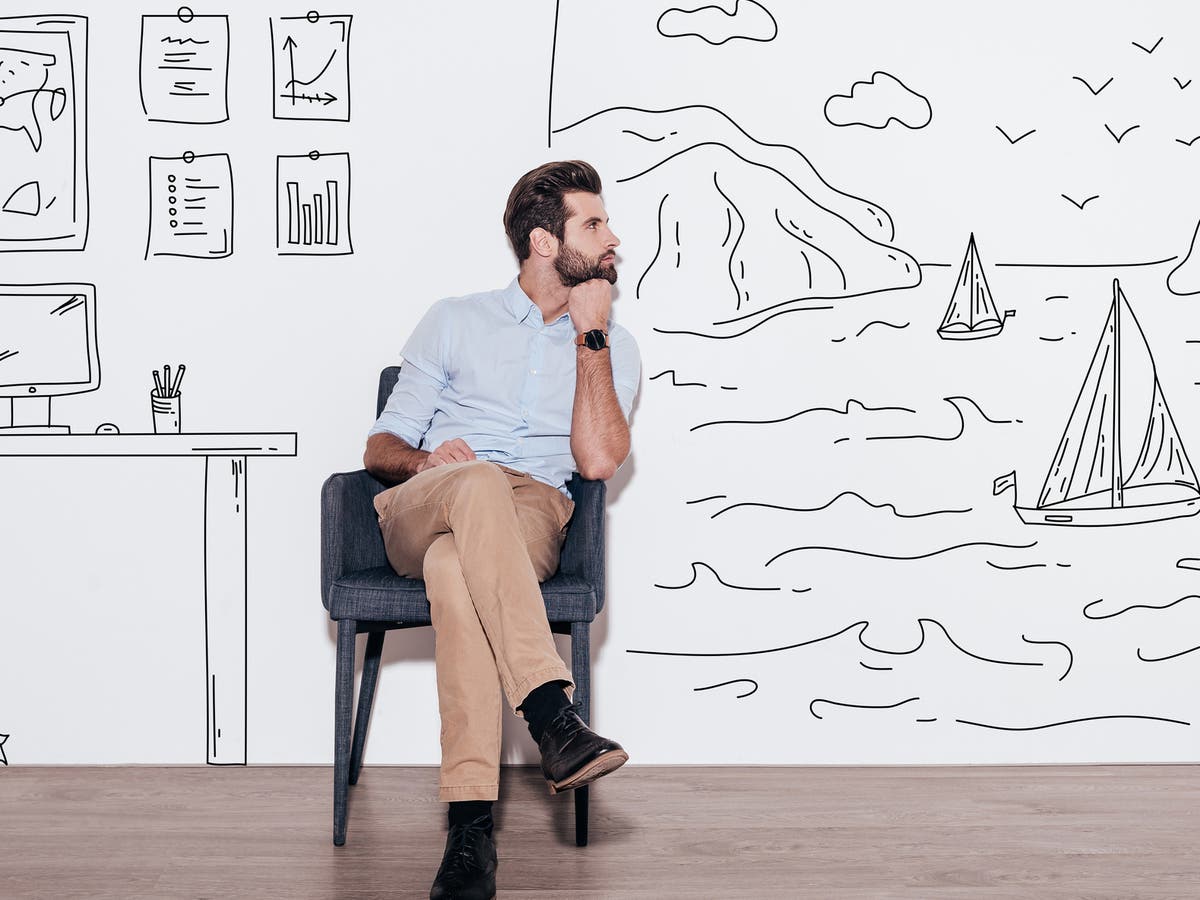

Daydreaming at work could carry ‘significant creative benefits’, research suggests The
Although daydreaming has some negative connotations, it actually has many benefits if done correctly, including boosting creativity and well-being. As a kid and young adult, Kristen Sobel was a.
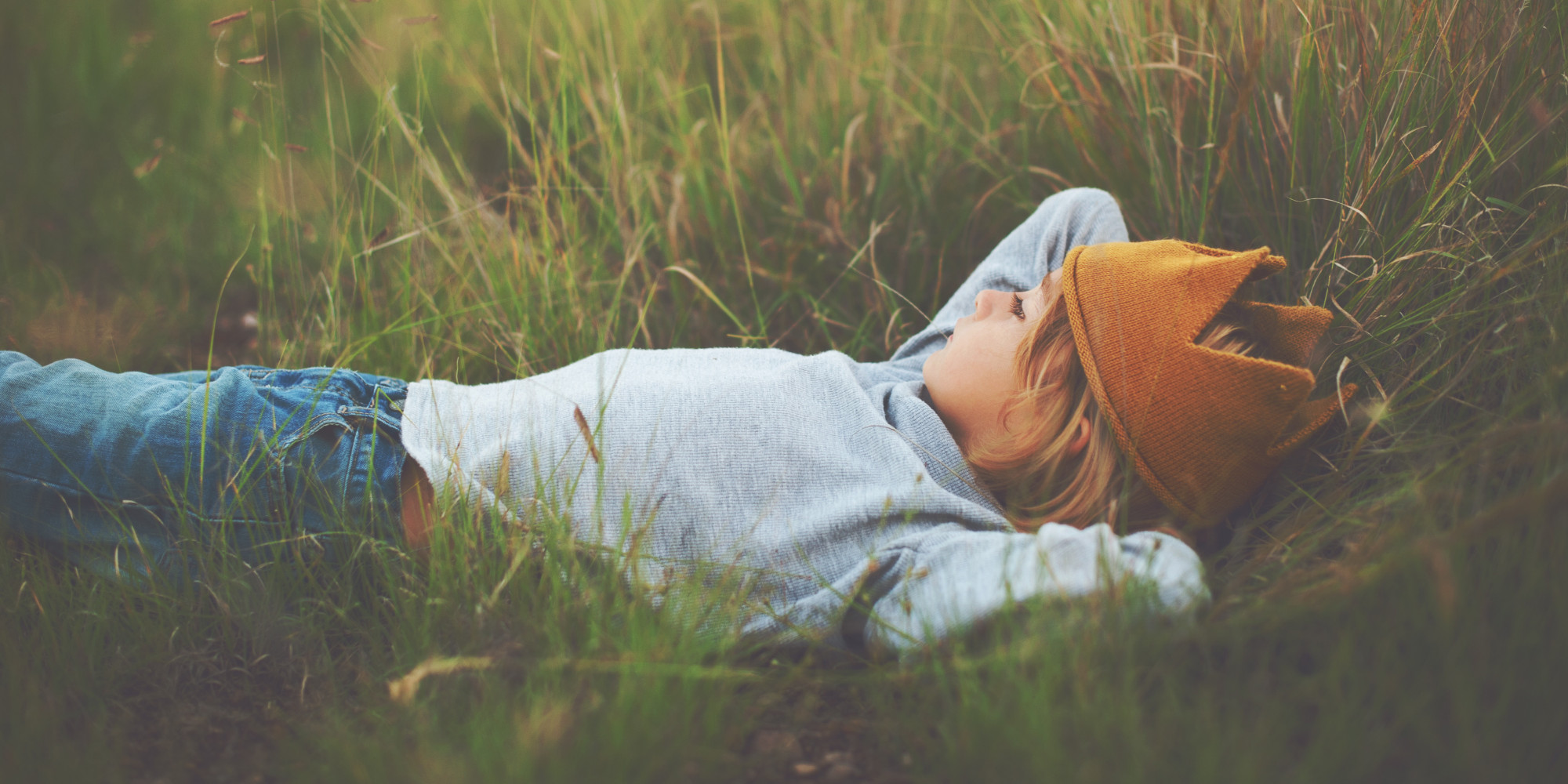

Why You Should Daydream More (In 3 Minutes) HuffPost
What's the stuff of daydreams? Your brain's default network may have the answer. Posted January 8, 2013Reviewed by Matt Huston Everyone, or nearly everyone, reports daydreaming on a regular.

The Power Of Daydreaming
When you are daydreaming (or mind-wandering, as it is more accurately referred to within scientific circles), memories that you thought were lost forever can come to the surface again, or you may suddenly find yourself realizing that you have forgotten someone's birthday — the kinds of things that don't happen when you are deep in concentration.
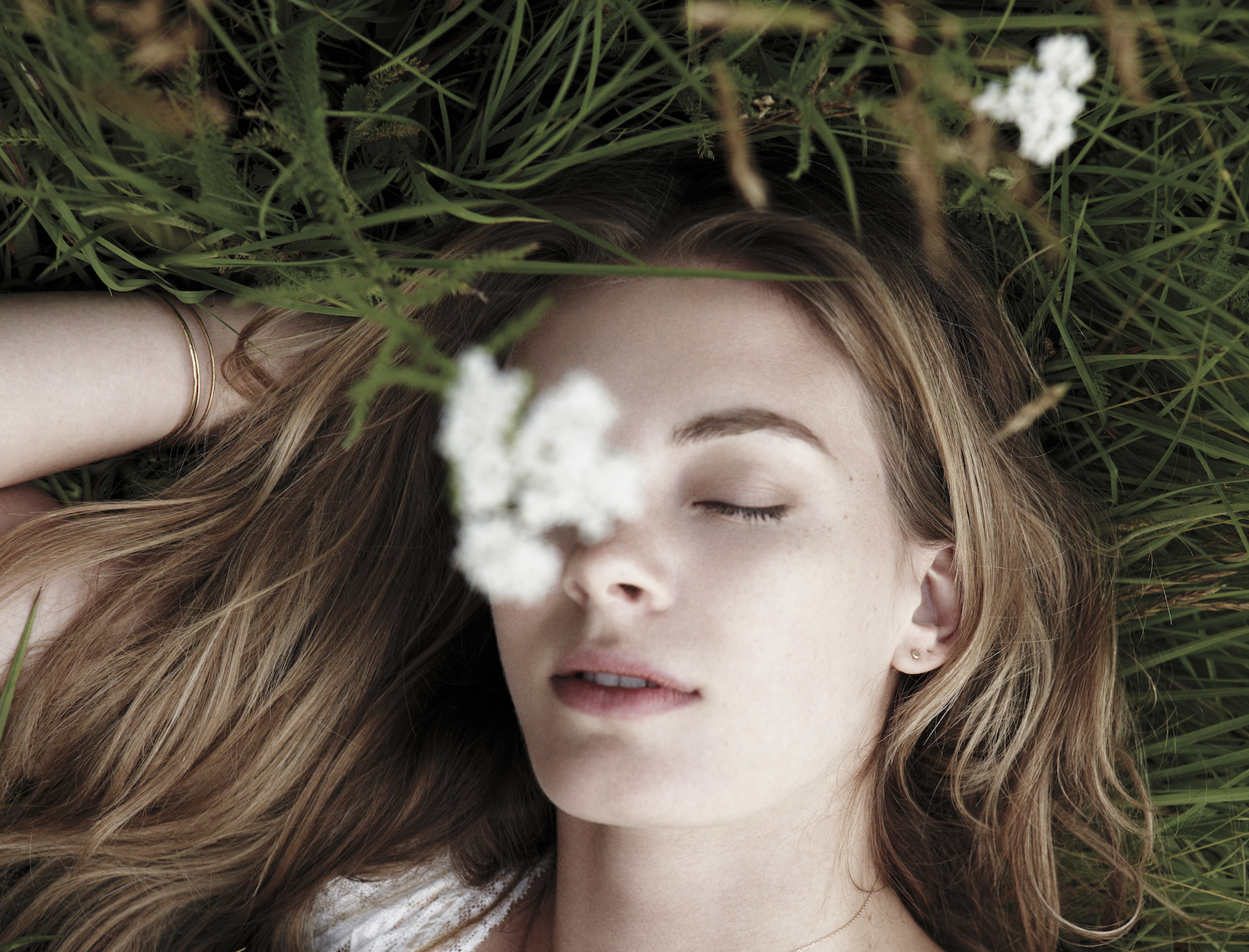

Why Daydreaming Is Productive goop
Dream therapy 'Escapist daydreaming occurs at times of stress, frustration or boredom, when we feel thwarted in the real world, and so remove ourselves to another, idealised, situation,' says Cliff Arnall, a psychologist who runs the No Pills practice in Wales.

Lisa Congdon Quote “Daydreaming is also important time for artists.”
Overview What is maladaptive daydreaming? Maladaptive daydreaming is a mental health issue where a person daydreams excessively, sometimes for hours at a time. "Maladaptive" means this type of daydreaming is an unhealthy or negative attempt to cope with or adapt to a problem.

What Is DAYDREAMING? DAYDREAMING Definition & Meaning YouTube
"Daydreaming can be an indication that someone is suffering from concentration difficulty, which is seen in many mental illnesses, including depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder,.

5 Positive Side of Daydreaming CareerGuide
When we consider that daydreaming is a hallmark of ADD/ADHD, one has to question if neurodivergent children are being labeled as "underachievers" or "troublemakers" for simply engaging in.

How to Stop Daydreaming and Start Living Your Life
Parts of the brain show sleep-like activity when your mind wanders. Our attention is a powerful lens, allowing our brains to pick out the relevant details out of the overwhelming flow of.

Daydreams are Powerful! Creative World School
They found the themes of "distraction from an unpleasant reality," "wish fulfillment," and "fighting boredom " to be the most commonly cited daydreaming themes. Other common themes.

8 Reasons to Encourage Your Child’s Daydreaming
Daydreaming — when our attention shifts to thoughts unrelated to our environment and experience — might seem like an easy escape from the here and now, but it can be a complicated mental task..
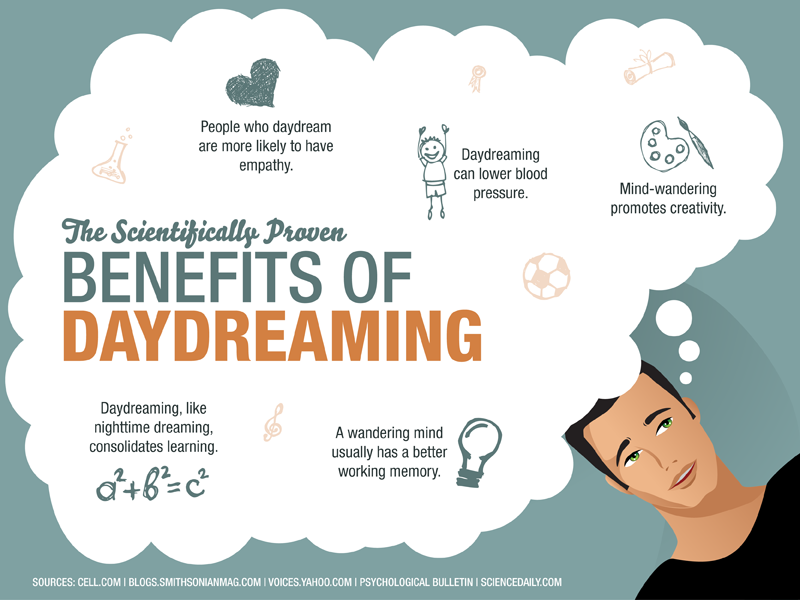
The Scientifically Proven Benefits of Daydreaming Naked Reverie
An overlooked brain region Scientists have spent considerable time studying how neurons replay past events to form memories and map the physical environment in the hippocampus, a seahorse-shaped brain region that plays a key role in memory and spatial navigation.

Scientists say daydreaming gives you a brain boost MiNDFOOD
Excessive daydreaming is often associated with anxiety, and some researchers have found that it may be linked to feelings of guilt, dysphoria, and inability to control your attention. Mental.