Chemical Burn On Lips Pictures
cause severe chemical burns to the surrounding mucosa when placed directly. Here, we describe a rare case of chemical burn caused by the direct placement of an aspirin tablet on a painful tooth. A 55-year-old healthy African female presented to the clinic with a history of pain in the right maxillary region. The patient stated that she had placed aspirin locally to relieve her toothache for a.

33426 Dentist Boynton Beach, Dental Care Boynton Beach, Dentistry
Aspirin-induced oral lesion: report of case. A case of aspirin burn on the posterior third of the hard palate is reported. Aspirin gum and aspirin tablets self-applied to the roof of the mouth produced local ulcerations within a week. When the local use of these two forms of aspirin was discontinued, the ulcerations healed.
Aspirin burn oral health tips and advices dentallifestyle
A white plaque-like lesion found in an area of irritation may be an aspirin burn due to "sucking" on an aspirin tablet or may be irritational keratosis due to constant irritation from a dental appliance (e.g., denture, orthodontic wire) or biting. Although these lesions do not rub off, they are not considered malignant.

How Long Will the Burning Mouth Syndrome? 6 Home Remedies for Burning Mouth Syndrome
Alternatively, a patient may hold an aspirin tablet directly in the mouth to relieve the pain of oral ulceration . Unfortunately, dissolution of aspirin in saliva produces a low pH and the net.

Placing an aspirin directly on your gum causes an ulceration of the tissue, commonly referred to
an aspirin tablet next to a painful tooth in the hope of providing relief from the pain. An aspirin burn develops when the acetylsalicylic acid's low pH of 3.3 induces epithelial necrosis.3 Aspirin burns are well described in the literature, including the notable case of a child with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis who sustained a mucosal burn.

What are the symptoms if Burning Mouth Syndrome? HTI CENTERS Medical Tourism Center
ASPIRIN BURN. Patients may sometimes place an aspirin tablet in the cheek in an attempt to reduce the regional pain of conditions such as aphthous ulcers, toothache, or thermal burn of the oral mucosa. Aspirin has a caustic effect on the oral mucosa, causing coagulation necrosis and formation of a region of white slough.

Montana Natural Gas Companies Does Aspirin Cause Gas
Aspirin is one of the most extensively used medications and has many beneficial effects. However, its injudicious use can produced local as well as systemic undesirable effects. A case of aspirin burn of the oral mucosa is presented. The lesion was in an unusual location. However, the history and th.
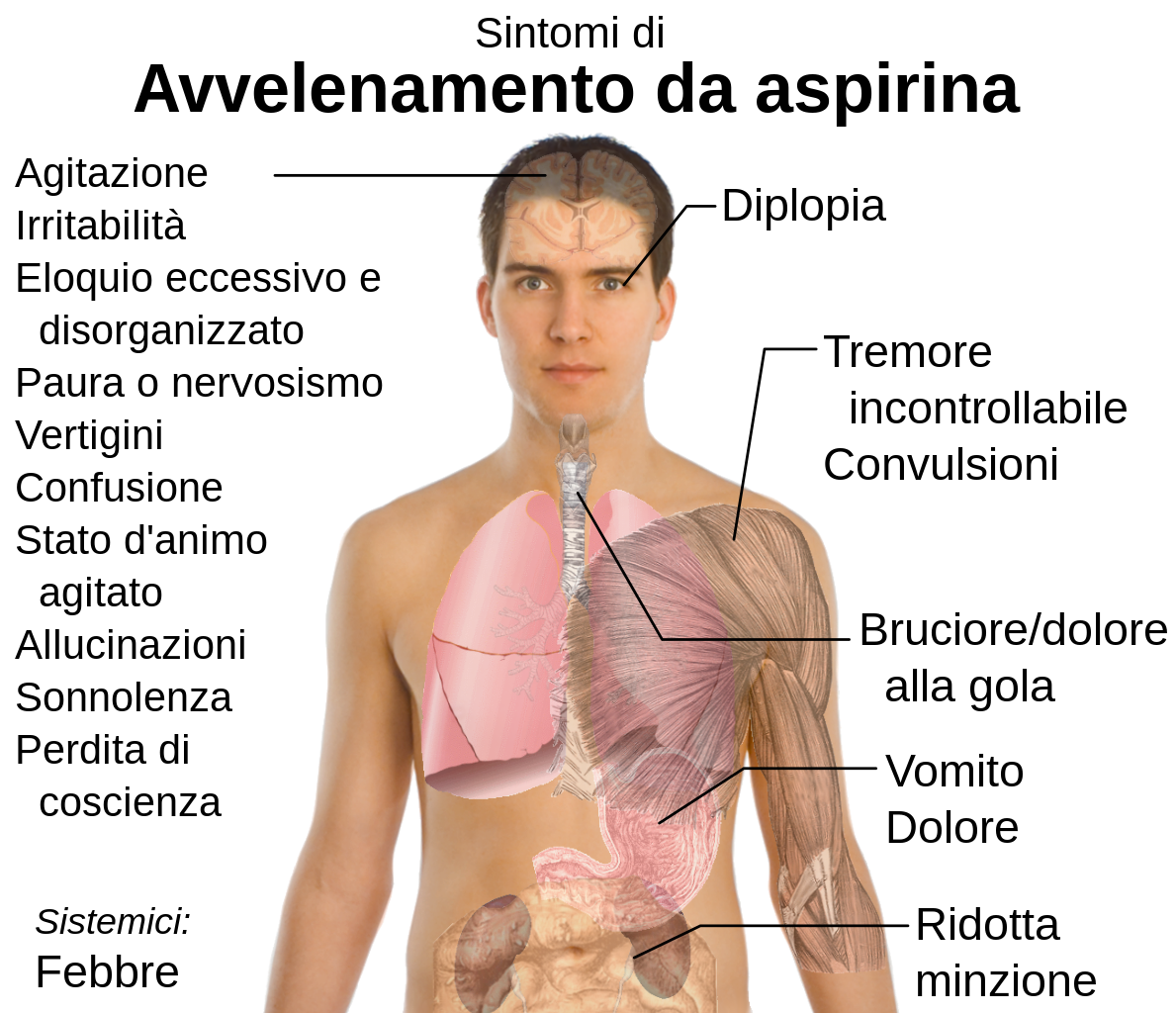
FileSymptoms of aspirin overdoseit.svg Wikipedia
Burning mouth syndrome has been defined as burning pain in the tongue or oral mucous membranes, usually without accompanying clinical and laboratory findings. 1, 2 In the past few years, some.

Oral burning burning mouth syndrome Medical Forum
A classic example of an oral chemical burn due to medication misuse is an aspirin burn. An aspirin burn most commonly is caused by the improper placement of an aspirin tablet next to a painful tooth in the hope of providing relief from the pain. An aspirin burn develops when the acetylsalicylic acid's low pH of 3.3 induces epithelial necrosis.

GOLDPHARMA Aspirin can save lives Goldpharma Medication
A 7-year-old boy reported to the department of pedodontics and preventive dentistry with the complaint of attached lower lip to the lower gums, difficulties in speaking, eating hot and spicy food and a burning sensation in the underlying mucosa. Upon inspection adhesion of the lower lip to the mandibular anterior vestibule, with a whitish appearance of the underlying mucosa was.

How To Get Rid Of Burning Mouth Syndromes Home Remedies For Burning Mouth Syndromes YouTube
Burns of the oral cavity may be caused by prolonged use of certain drugs by the patient or by incorrect use of caustics by the dentist. Unwillingly-acquired self-inflicted injuries are also encountered, such as caustic ingestion (out of curiosity or by accident), excessive consumption of fresh fruit and fresh fruit juice, and wrong oral hygiene practice.

Can You Cure a Toothache by Putting an Aspirin On It? Oral Answers
hyperventilation. irritability. shaking. stomach discomfort, upset, or pain. trouble sleeping. unusual drowsiness, dullness, tiredness, weakness, or feeling of sluggishness. Other side effects not listed may also occur in some patients. If you notice any other effects, check with your healthcare professional.
Infection Of Ulcer Inside Mouth Stock Image Image of aspirin, hygiene 80070969
Aspirin-induced oral lesions are chemical burns caused by the placement of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) directly on the oral mucosa in an attempt to alleviate pain. Epidemiology Traumatic fibromas can occur in any patient population; however, it has a predilection for middle-aged females. [7]

Aspirin induced intraoral burn A rare case report with emphasis on its diagnosis Semantic Scholar
Aspirin burn of the oral cavity. Ann Pharmacother. 1998; 32: 1107.. Aspirin can cause severe damage to both the hard and soft tissues of the mouth. Chewable aspirin products still are popular analgesics. Dentists should counsel patients about the dangers from aspirin to the oral mucosa and teeth. If the patient cannot or will not discontinue.

PPT Cheek chewing PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2413507
From the casebook - aspirin burn. N YJ Dent 1977; 4 7: 310. Google Scholar. Hille J J . A fruit mouth-wash chemical burn. Report of a case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1984; 58:.
Aspirin, Clonidine Fail to Halt Nephropathy After Surgery
Patients experiencing toothache may place an aspirin tablet adjacent to the affected tooth in an attempt to relieve the pain. Dissolution of aspirin in saliva produces a low pH, which leads to a local chemical burn on the mucosa, referred to as an "aspirin burn" with little, if any, relief of the toothache. Patients should be advised.