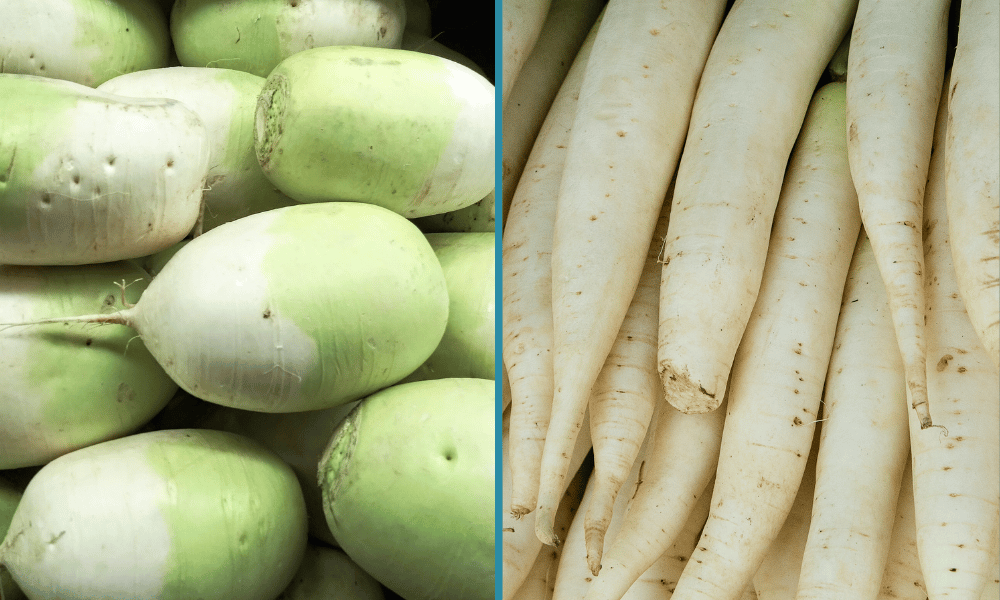
Korean Radish vs Daikon What's the Difference? Let's Foodie
The forage radish-also known as oilseed radish, groundhog radish, and the trademarked tillage radish-has gained in demand with farmers looking for the no-till method. The thick upper part of the radish can root in the dirt over 20 inches. The taproot can go further, reaching several feet! The method, called "bio-drilling", breaks up.

Radish vs Turnip Differences and Nutrition Good Recipe Ideas
Final Thoughts. Tillage radish proves to be an exceptional cover crop for enhancing soil health and fixing clay and compacted soils. Its deep root and taproot aid in soil aeration, nutrient cycling, and compaction alleviation. Tillage radish breaks up compacted soil, improving its structure and promoting better water infiltration.

Cover Crops Tillage Radish vs. Oilseed Radish RealAgriculture
The extra long, 10-20 inch roots of Groundhog allows it to drill down and pull huge amounts of nutrients from deep within the soil, which the following crop can utilize. In just 6-8 weeks, Groundhog can capture 150-200 pounds of nitrogen per acre before winter killing. Plant in late summer. Recommended seeding rate: ½ pound per 1000.

Korean Radish vs Daikon Fanatically Food
The forage brassica has big-time potential for rejuvenating tired, compacted pastures — but there's a learning curve. By. Alexis Kienlen. Reading Time: 3 minutes. Published: September 25, 2015. Livestock, Pasture. Tillage radishes bring many benefits, but "we're learning as we go," says Clearwater County official Annie Bertagnolli.
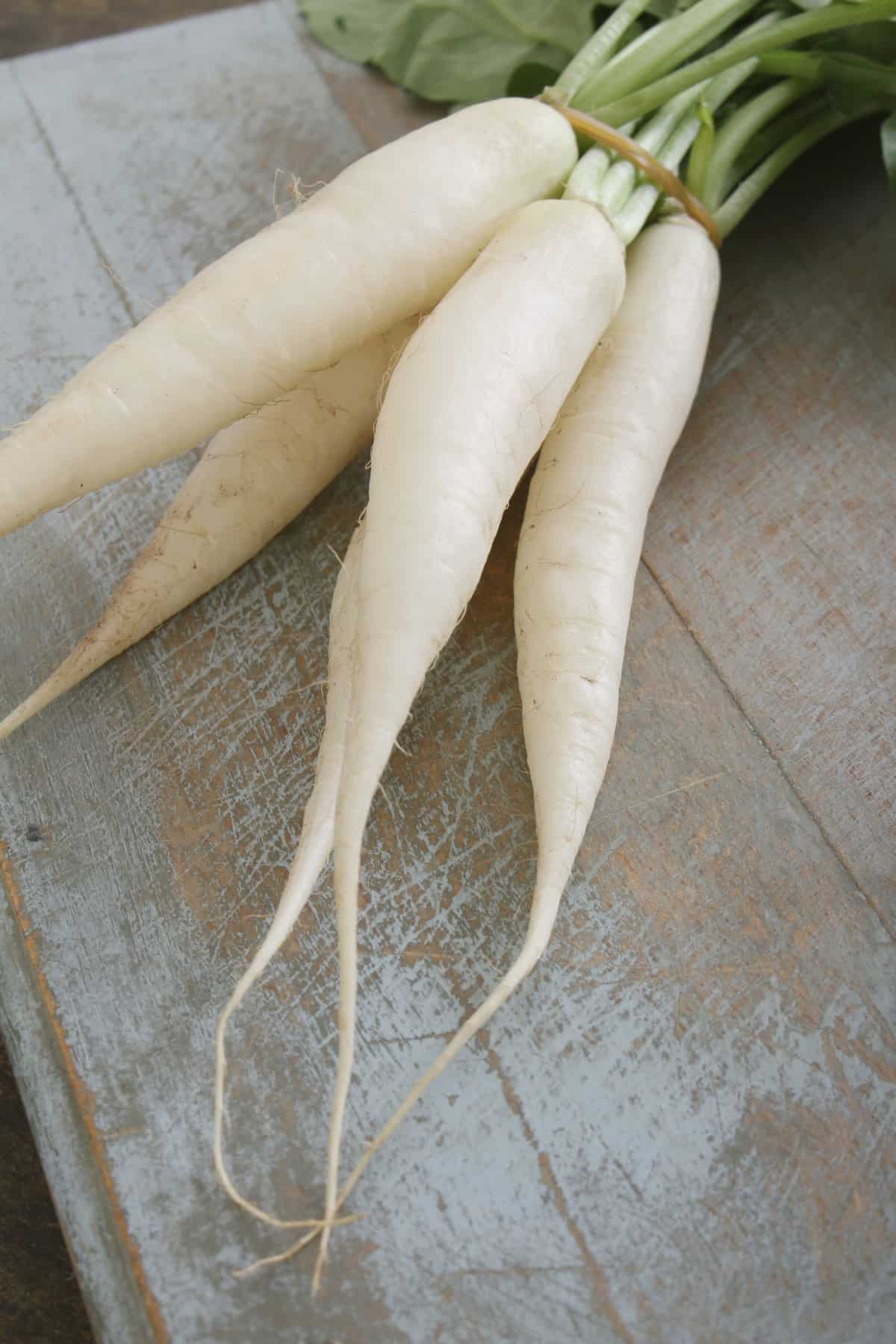

What is Daikon Radish? How Do I Eat It? Noshing With the Nolands
The tillage radish or daikon radish has been bred and developed to produce a large taproot and penetrate compacted soil layers to increase soil aeration and water infiltration, to decrease compaction and to increase rooting depth opportunities for successive crops. Tillage radishes are often promoted to help alleviate compaction, but they do.

The Difference Between Daikon Radish And Horseradish Thoroughly
Cover crops. Nature's way of tilling and conserving soil. It's a non-traditional approach that South Texas farmer Zack Yanta uses to improve soil health and.
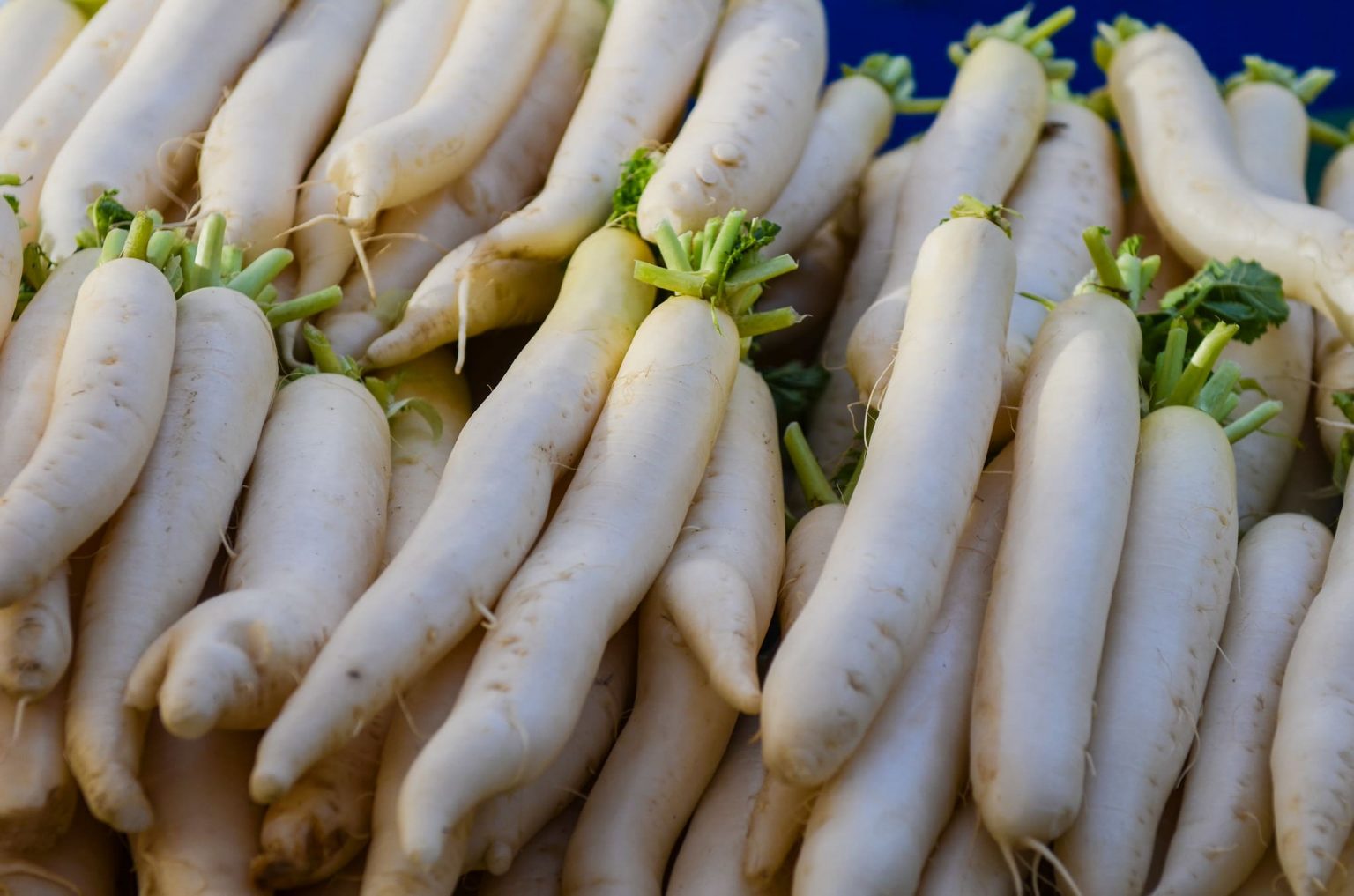

Radish Daikon Nutrition Facts, Health, Consumption and Recipes
When it comes to the world of radishes, two varieties that often cause confusion among gardeners and agricultural enthusiasts are Tillage Radish and Daikon . Exercise; Healthy Eating; Weight Loss; Well-being; Stress; Sleep; Illness; Write for Us; Archives. December 2023; November 2023; October 2023; September 2023; August 2023;
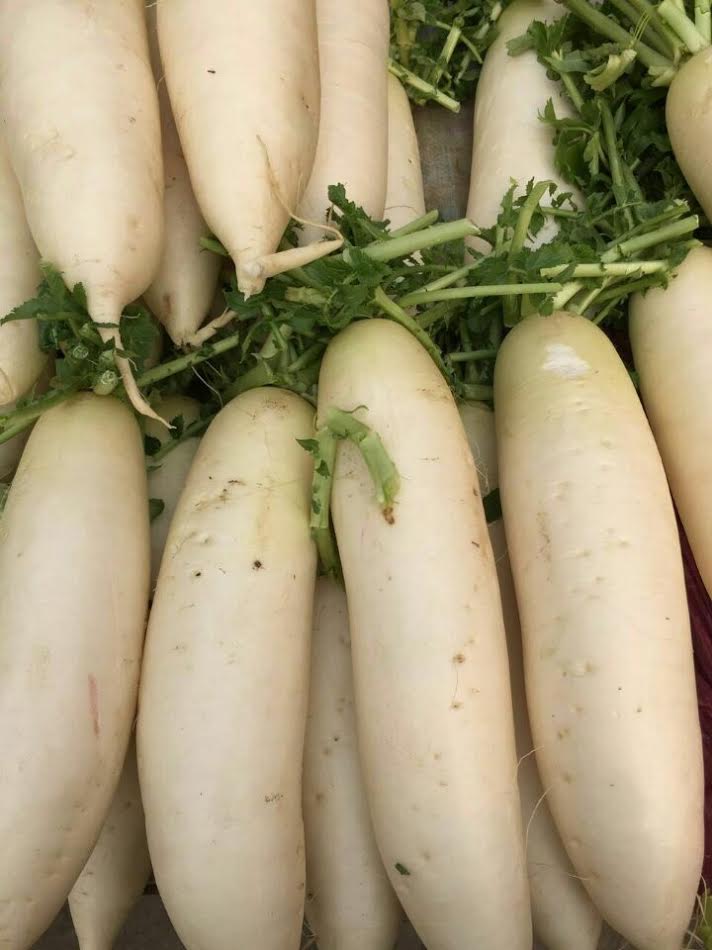

Easy Daikon Radish Recipe 2023 AtOnce
August 7, 2022. In Vegetables. Daikon in Japanese means large root. There are perhaps hundreds of varieties of daikon radishes bred for different purposes: from the very mild carrot-shaped types for fresh eating and pickling, to the tillage types we sell here. This strain of daikon is referred to as a biodrill or tillage radish.
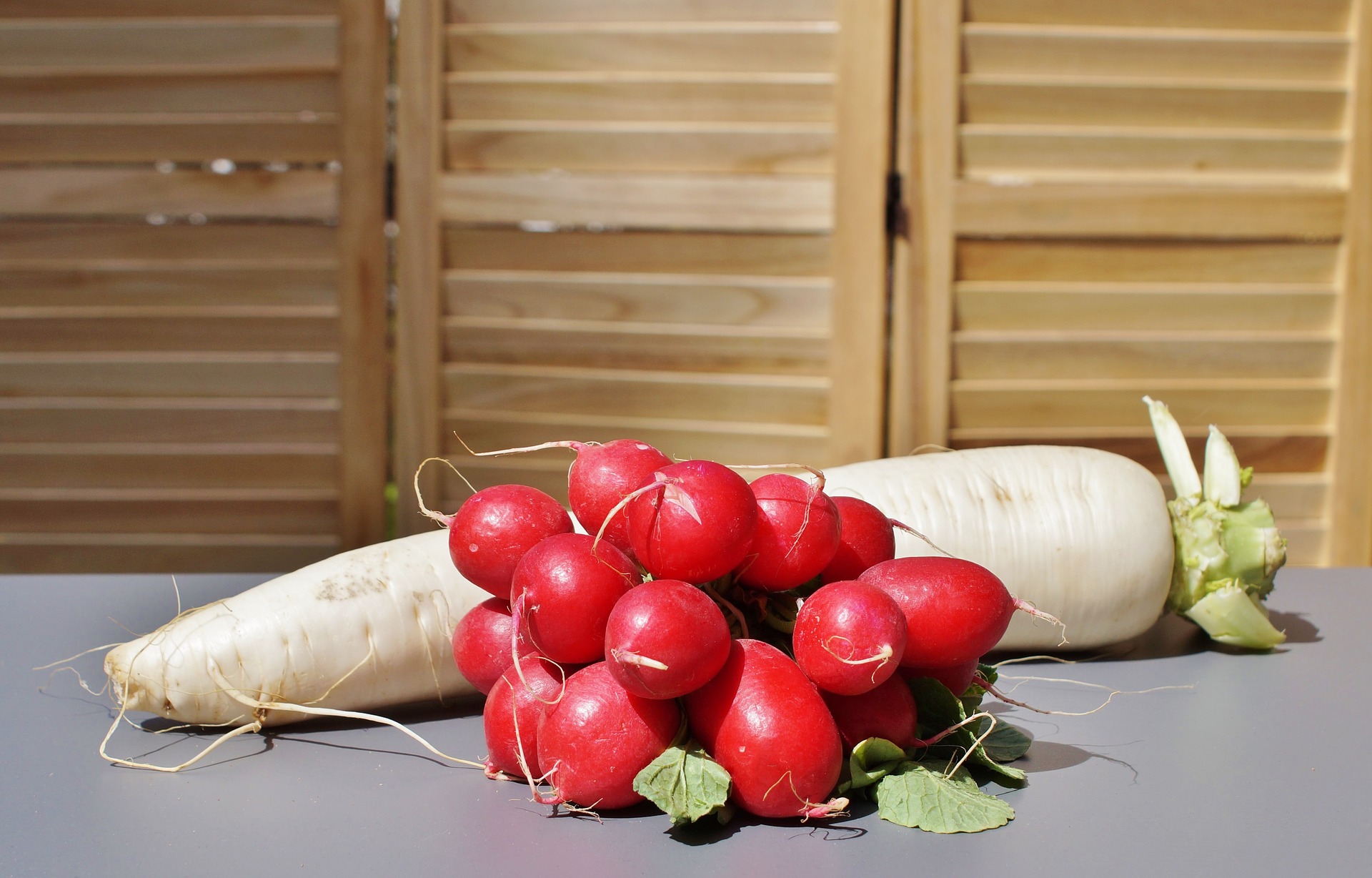

Difference between radishes and daikon radishes
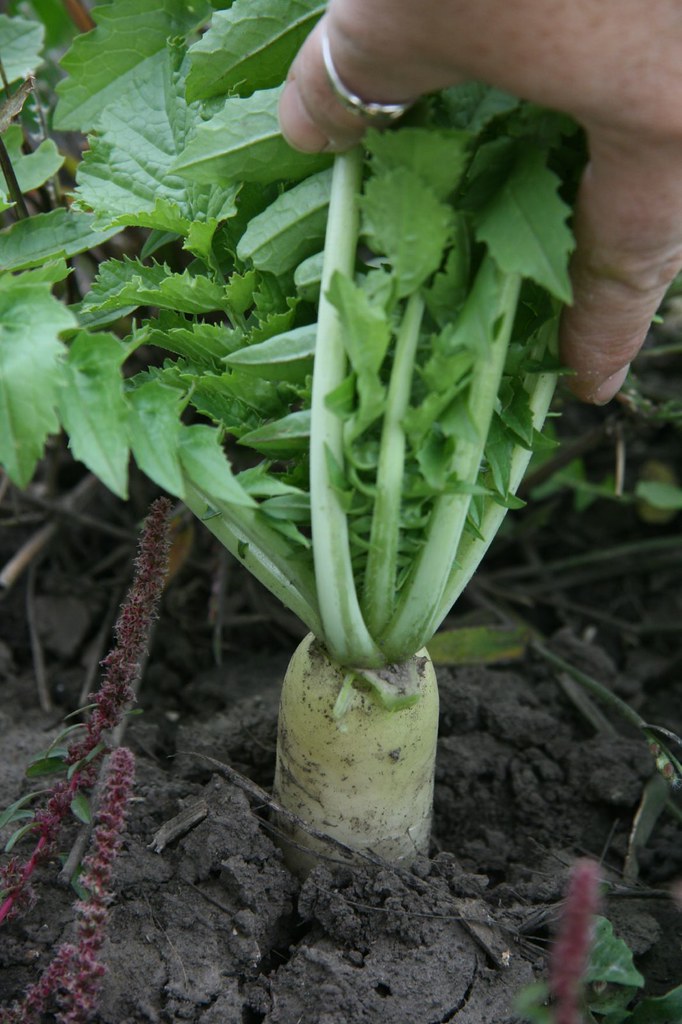
General Comments. Radish (e.g., Tillage, Groundhog, Nitro, oilseed or forage radish) is a fast growing edible root vegetable capable of producing a girthy taproot that can extend several feet deep if planted in July or August. Daikon radishes selected as cover or forage crops are often touted to alleviate soil compaction by "bio-drilling" down through compacted layers within the crop root.

tillage radish Otherwise known as daikon. cheeses Flickr
Biodrilling up to six feet below the soil surface, daikon radish is nature's rototiller. It breaks through hard, compacted soil layers that have broken many a gardener back. It mechanically opens up channels for water and roots to penetrate. But unlike your rototiller, daikon fills the holes it drills with pounds and pounds of delicious.

Radish (Tillage, Groundhog, Nitro, oilseed or forage radish) Cover
Nitro Daikon Radish produces more root mass than oil seed radish. This large root system will pull nitrogen and nutrients deep within the soil and bring them back to the surface. Establish very quickly, providing good ground cover preventing erosion. Radish cover crop captures 150 to 200 pounds of nitrogen per acre before winter killing.

Differences between Daikon and Radishes
Tillage radishes are daikon radishes with a thick white tuber that can grow up to 18 inches in length, and a single long taproot that can easily bring the plant's total rooting depth to four feet or more. Very aggressive when rooting, tillage radishes can exert 290 pounds per square inch of pressure as they drill down, which allows them to.
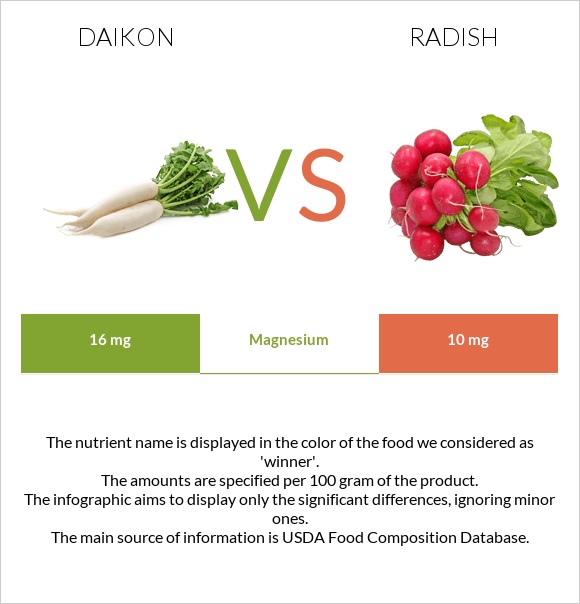
Daikon vs Radish InDepth Nutrition Comparison
The tillage radish or daikon radish has been bred/developed to produce a large taproot and penetrate compacted soil layers in an effort to increases soil aeration, water infiltration, decrease compaction and provide increased rooting depth opportunities to successive crops. Tillage radish are often promoted to help alleviate compaction, but do not do well in poorly-drained soils that are prone.
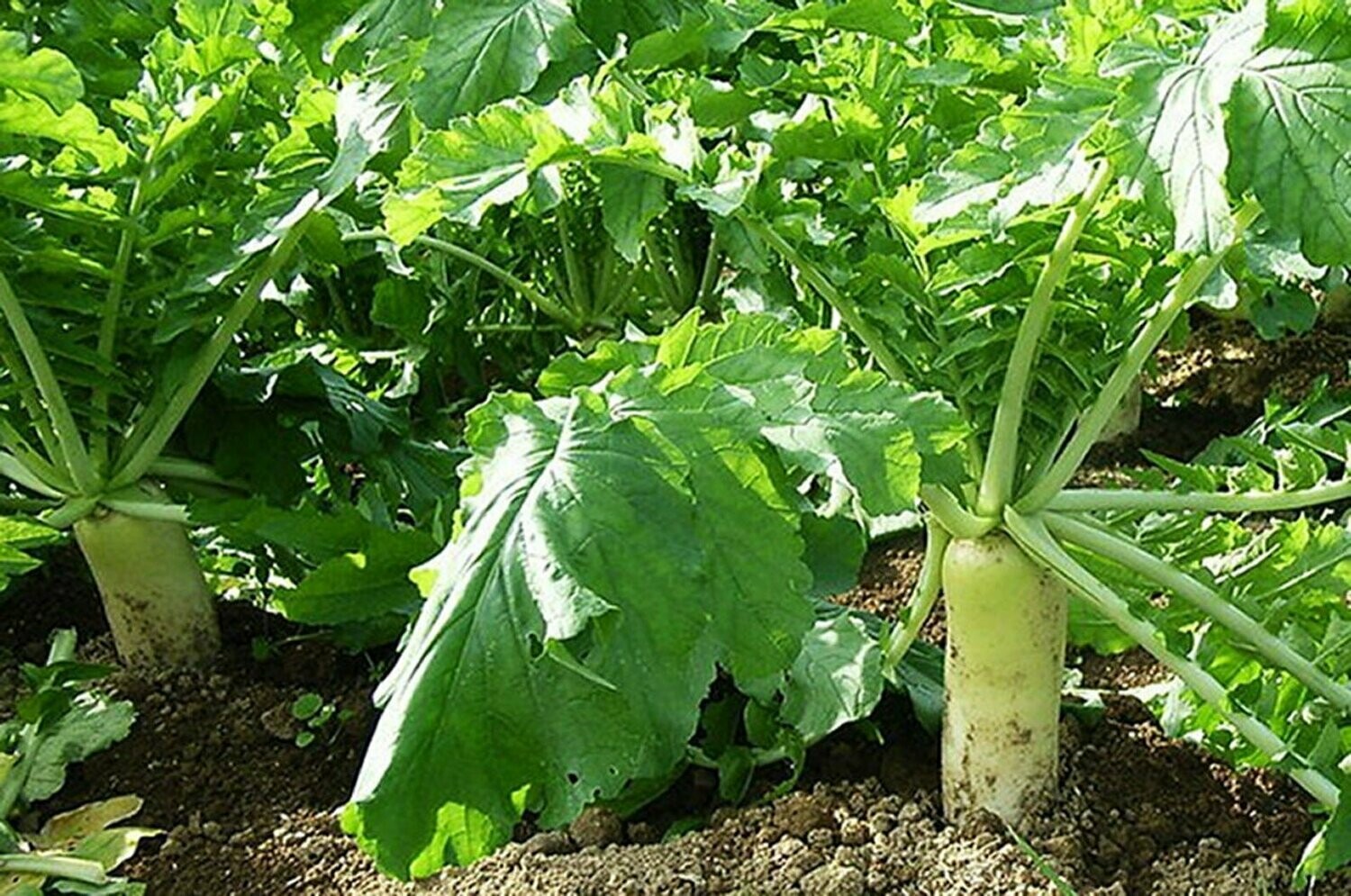

Fracking Daikon (Tillage) Radish (Raphanus sativus)
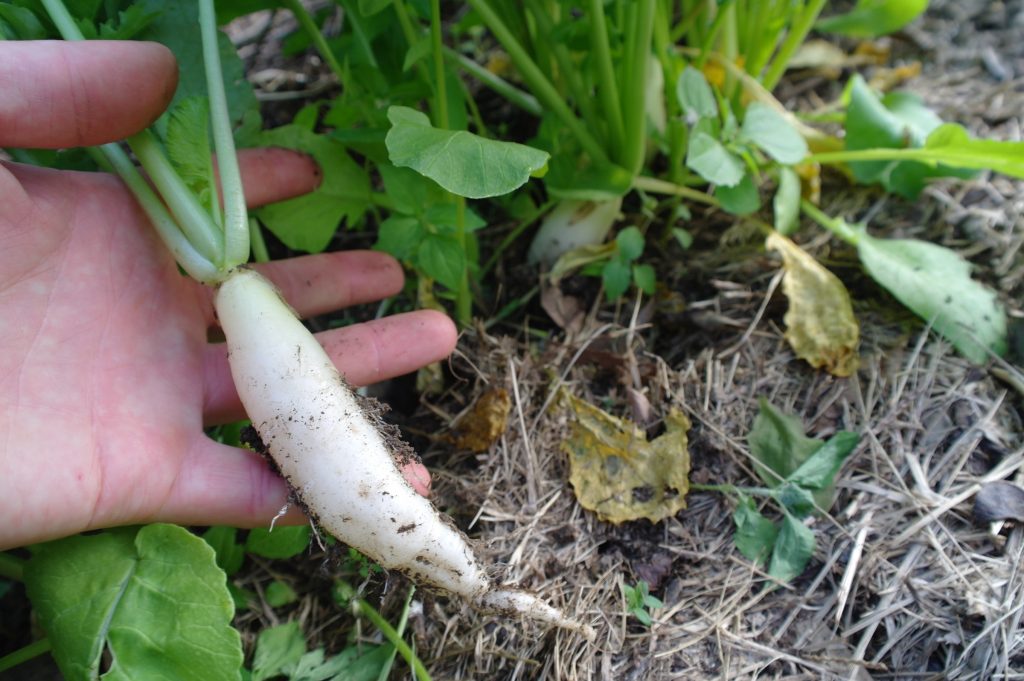
Bottom picuture is the difference between daikon radish and a graza fodder radish, used more for grazing. Daikon is the type or species. Tillage radish is the trade marked name for the variety. Tillage radish is a daikon. But the experts will come along soon and correct that if need be.

Tillage Radish Cover Crop
Daikon has more carbs than radishes. The vitamin levels in these veggies are similar, but daikon has a higher percentage of vitamin C and folate, whereas radishes are high in vitamin K and B6. Comparatively, daikon is high in minerals like phosphorus and magnesium, but both vegetables are similar in calcium and potassium.

What Is Daikon? The Crispest, Coolest Vegetable We Know Bon Appétit
The daikon radishes are seeded in a cover crop mixture with eight or nine other seed varieties. The cover crop isn't taken as hay, or grazed, but left to grow as a type of green manure. While.