
Edward Tylor
Edward Burnett Tylor,. near his peak of his reputation and influence as the leading British anthropologist of the nineteenth century.' [Stocking, 1995: 3] Tylor emerged as the pre-eminent British anthropologist of the later nineteenth century.' [Stocking, 1995: 11]

119 Edward Tylor Stock Photo Alamy
Animism as an anthropological concept was launched by British evolutionary anthropologist Edward Burnett Tylor (1832-1917), whose two-volume book Primitive Culture (1871) was extremely influential for over three decades in Britain and beyond. Tylor's ideas were followed by armchair anthropologists, folklorists and other scholars interested in comparing "savagery" to "civilization.

Sir Edward Tylor Photograph by Granger Fine Art America
Edward Burnett Tylor was born in 1832 and at the age of sixteen joined his family's brass foundry. In 1855 he showed signs of tuberculosis and was sent on a trip to the United States of America, Cuba and Mexico. It was during this trip that he famously became interested in anthropological and archaeological matters.

Antr 3005 Clase 8
Edward Burnett Tylor (1832-1917) may not be a household name today, but during the second half of the nineteenth century the Victorian anthropologist and scientific naturalist was a figurehead for anthropology throughout the British Empire. At his seventy-fifth birthday in 1907, his former student and friend Andrew Lang (1844-1912) argued that 'he who would vary from Mr. Tylor's ideas must.

Unilinear Evolutionism
Edward Burnett Tylor in his Primitive Culture (1871). Tylor believed that seemingly irrational customs and beliefs, such as peasant superstitions, were vestiges of earlier rational practices.

Edward Tylor Celebrity biography, zodiac sign and famous quotes
Abstract. Edward Burnett Tylor (1832-1917) is often considered the father of anthropology. This chapter presents Tylor's main theories in the field of anthropology. One of Tylor's major areas of interest was the use of anthropological evidence to discover how religion arose. This preoccupation resulted in his influential account of animism.
Edward Tylor
Abstract. Edward Burnett Tylor's (1832-1917) theory of survivals, or elements of the "primitive" or archaic past that continued to play an active part in the beliefs of the present day, hallmarks the Victorian effort to isolate and display what were thought to be the most developed features of the contemporary world.

Tylor and technology
Edward B. Tylor disagreed with the contention of some early-nineteenth-century French and English writers, led by Comte Joseph de Maistre, that groups such as the American Indians and other indigenous peoples were examples of cultural degeneration.

Interculturalidad en salud
Sir Edward Burnett Tylor (born Oct. 2, 1832, London—died Jan. 2, 1917, Wellington, Somerset, Eng.) English anthropologist regarded as the founder of cultural anthropology.

EDWARD TYLOR (18321917). Pionero en la antropología que en 1871 definió el concepto de
Edward B. Tylor, founder of the study and curriculum of anthropology, is considered to be the first cultural evolutionist anthropologist and the father of the science of anthropology. Tylor was born the son of Quakers on October 2, 1832 in London, England.

Anth1 Theory Ch03
Sir Edward Burnett Tylor FRAI (2 October 1832 - 2 January 1917) was an English anthropologist, and professor of anthropology. [1] Tylor's ideas typify 19th-century cultural evolutionism.
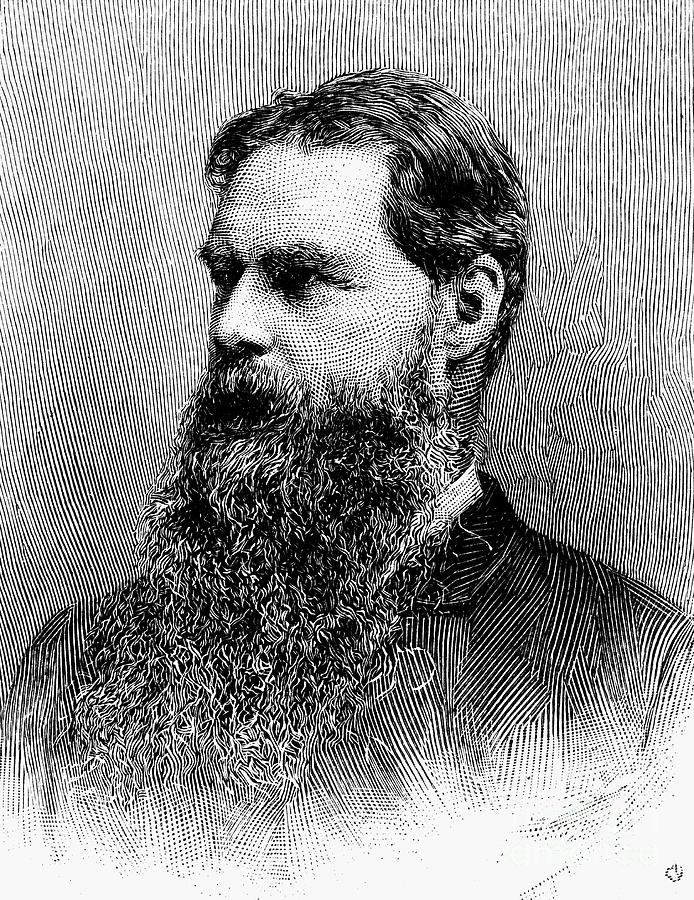

Sir Edward Tylor Photograph by Granger
Edward Burnett Tylor was born in 1832 and at the age of sixteen joined his family's brass foundry. In 1855 he showed signs of tuberculosis and was sent on a trip to the United States of America, Cuba and Mexico. It was during this trip that he famously became interested in anthropological and archaeological matters.

Javier Prieto González Ciencias etnográficas y Sociología.
Edward Burnett Tylor, Religion and Culture is a welcome reappraisal of an under-studied pio- neer of the anthropology of religion. E. B. Tylor (1832-1917) was the first reader in social anthropology at Oxford University in 1884, and became the first professor of the subject in 1896.

edward tylor Latest news, Breaking news headlines Scoopnest
Sir Edward Burnett Tylor (October 2, 1832 - January 2, 1917), was an English anthropologist, often regarded as the founder of cultural anthropology. Tylor began his studies during travels recommended for his health, where he encountered cultural differences and joined archaeological investigations of prehistoric human societies.

Edward Tylor Quotes. QuotesGram
Edward Burnett Tylor (1832-1917) is often considered the father of the discipline of anthropology. Despite such eminence, his biography has never been written and the connections between his life and his work have been largely obscured or ignored.
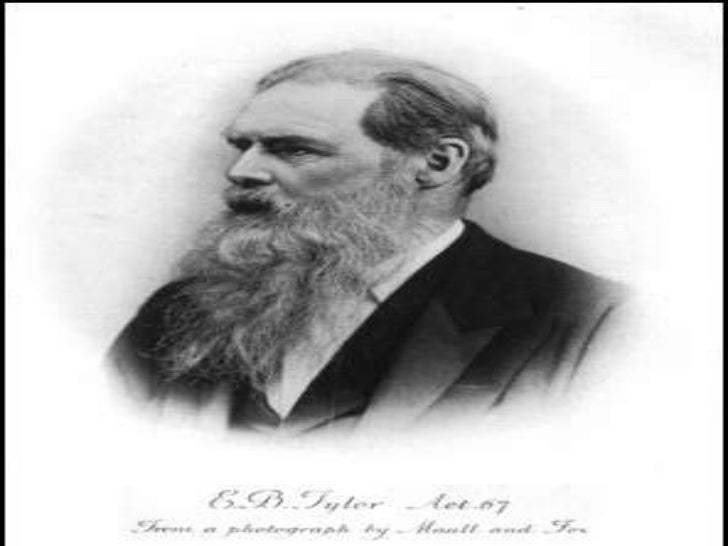

Edward Tylor
Edward Burnett Tylor (1832-1917) was an English anthropologist who is widely considered the founder of anthropology as a scientific discipline. He was the first Professor of Anthropology at the University of Oxford from 1896 to 1909, and developed a broad definition of culture which is still used by scholars. First published in 1871, this.