
We have a wide variety of columns and column wraps available. House with porch, Porch remodel
For this Classical Comments piece we will deal with some architectural minutiae—the transition from Roman-style moldings to Greek ones that took place in the late 18 th century. Until the publication in 1762 of the first volume of James Stuart and Nicholas Revett's The Antiquities of Athens virtually all 18 th-century molding profiles in both Britain and America adhered strictly to ancient.

DIY Guide To Decorative Mouldings
The base: In some of the oldest columns, including Egyptian and early Doric in Greece, the columns have no separate base but are placed directly on the floor or pavement. But most columns have a rectangular or square base molding, the lowest part of which is the plinth. The base molding can be quite varied, including for example the semi-circular torus and the ring called the cincture which.

Architectural Moulding Planes by Gleave
F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W Z See also Notes References A Abacus A flat slab forming the uppermost member or division of the capital of a column. Accolade A sculptural embellishment of an arch. Aisle The subsidiary space alongside the body of a building, separated from it by columns, piers, or posts. Ante-choir

Dentil Mouldings Cornice design, Dentil moulding, House designs exterior
Or, it can be expressed as a spiral. Every square and rectangle = the same ratio which 1:1.618. It is easy for me to remember because my son's birthday is 6.18. :] Did you know that the ratio from the floor to your navel (1) and then from your navel to the head (.618) is roughly 1: 1.618. There you go.

Architectural Mouldings Architectural Moldings Latest Price, Manufacturers & Suppliers
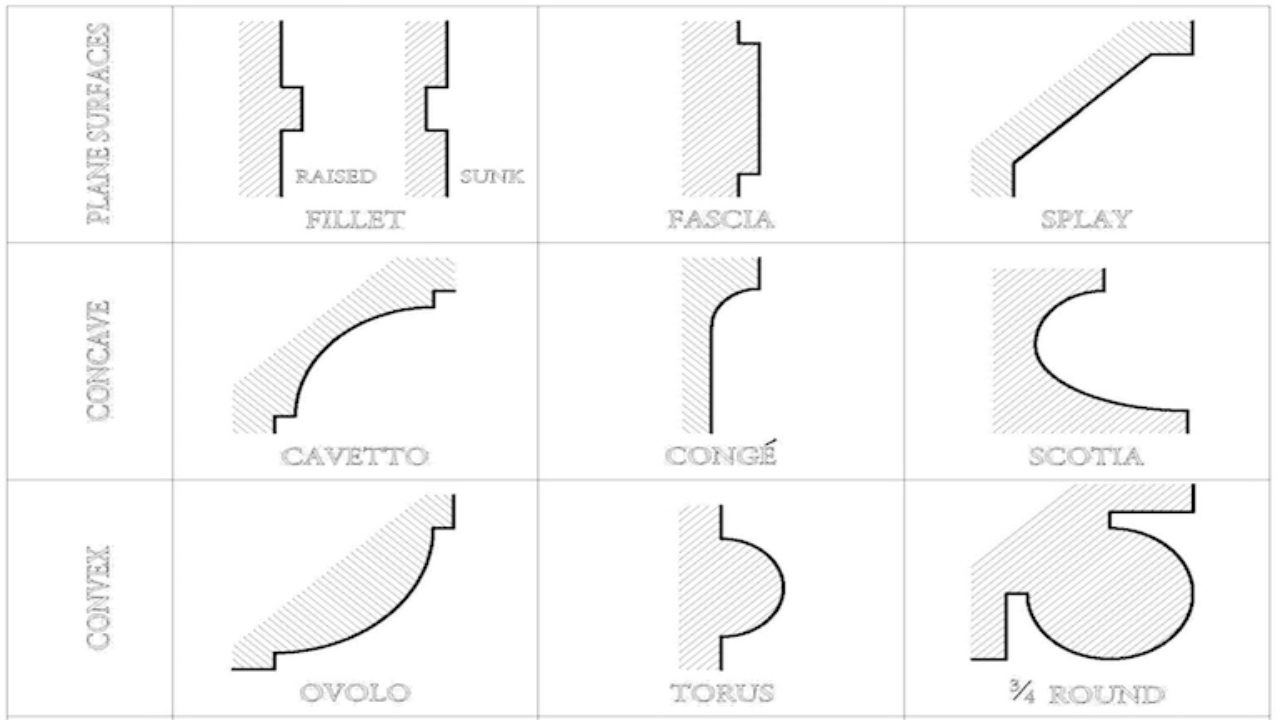
between a convex moulding and a flat member. Also used to afford shadow to an ogee or ovolo. Reeding A form of surface decoration, consisting of parallel convex mouldings Scotia A small concave moulding between the two tori in the base of a column. It throws a deep shadow. Torus (plural: tori) A bold convex moulding used in the bases of columns.

Architectural Columns Toronto Elite Moulding 416.245.1115
Glossary of Architectural Terms — Adrian Architecture Illustrated Glossary By Peter Barr Selected Architecture Terms from top to bottom: Towers Dormers Roofs Eaves Cornices Walls Windows Porches Columns Foundations Towers Towering above many Italianate, Octagon and Queen Anne homes are campaniles and cupolas.

The Origin of Mouldings The Victorian Emporium
Scotia is a type of architectural molding that is commonly used to cover the joint between a curved wall and a flat ceiling. It is a concave molding that. It is used to create a transition between the column and the base or to soften the transition between two different materials. Trochilus, on the other hand, is a convex molding that is.
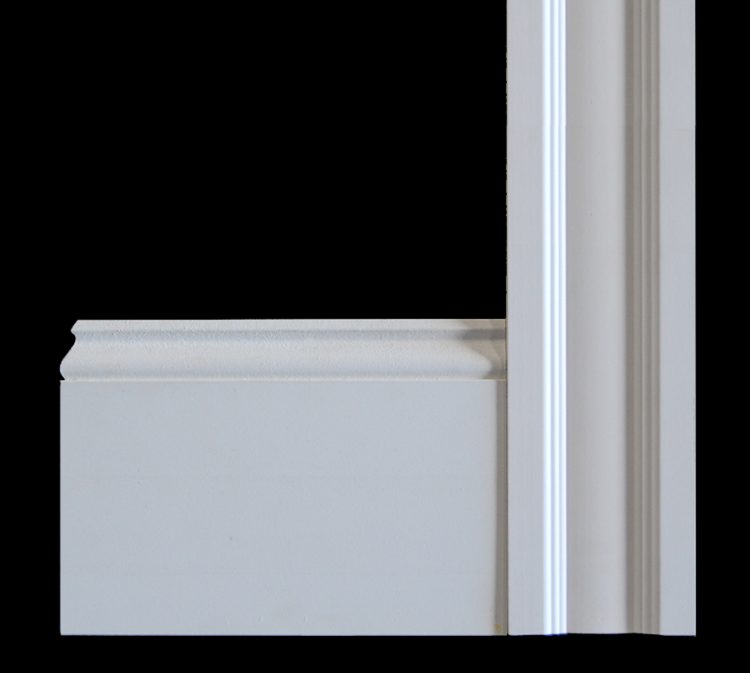

imagemouldingbase2 Builders Surplus
Let's find possible answers to "Architectural moulding at the base of a pillar" crossword clue. First of all, we will look for a few extra hints for this entry: Architectural moulding at the base of a pillar. Finally, we will solve this crossword puzzle clue and get the correct word. We have 1 possible solution for this clue in our database.

Ode to a Tuscan Column Accident or Experiment in the Canon of Bad Trad Tuscan column, Design
In architecture a base is the lowest part or lowest main division of a structure. For columns, the base is the lowest portion of three parts, from top to bottom: the base, the shaft and the captical. Typically, Egyptian columns and Greek Doric columns have no base and are placed directly on the floor.
The Elements of Classical Architecture Introduction to Mouldings Institute of Classical
Today's crossword puzzle clue is a general knowledge one: Architectural moulding at the base of a pillar. We will try to find the right answer to this particular crossword clue. Here are the possible solutions for "Architectural moulding at the base of a pillar" clue. It was last seen in British general knowledge crossword.

Architectural Moulding High Profile Architectural Mouldings
A plinth is a base or platform that supports a pedestal, column, or structure. It's not only a simple architectural element, but also a very important one. It's not only a simple architectural.
Mouldex Architectural Moulding Architrave Pwa093 92h X 32w X 3000mm
The solid part of a pier or wall, etc. against which an arch abuts, or from which it immediately springs - acting as a support to the thrust (or lateral pressure). The abutments of a bridge are the walls adjoining to the land, which supports the ends of the roadway, or the arches at the extremities.

DIY Guide To Decorative Mouldings
Fluting (architecture) Concave fluting on Doric order columns; Northington Grange, a Greek Revival building of 1804-1817. Fluting in architecture and the decorative arts consists of shallow grooves running along a surface. The term typically refers to the curved grooves (flutes) running vertically on a column shaft or a pilaster, but is not.

Pin on Columns
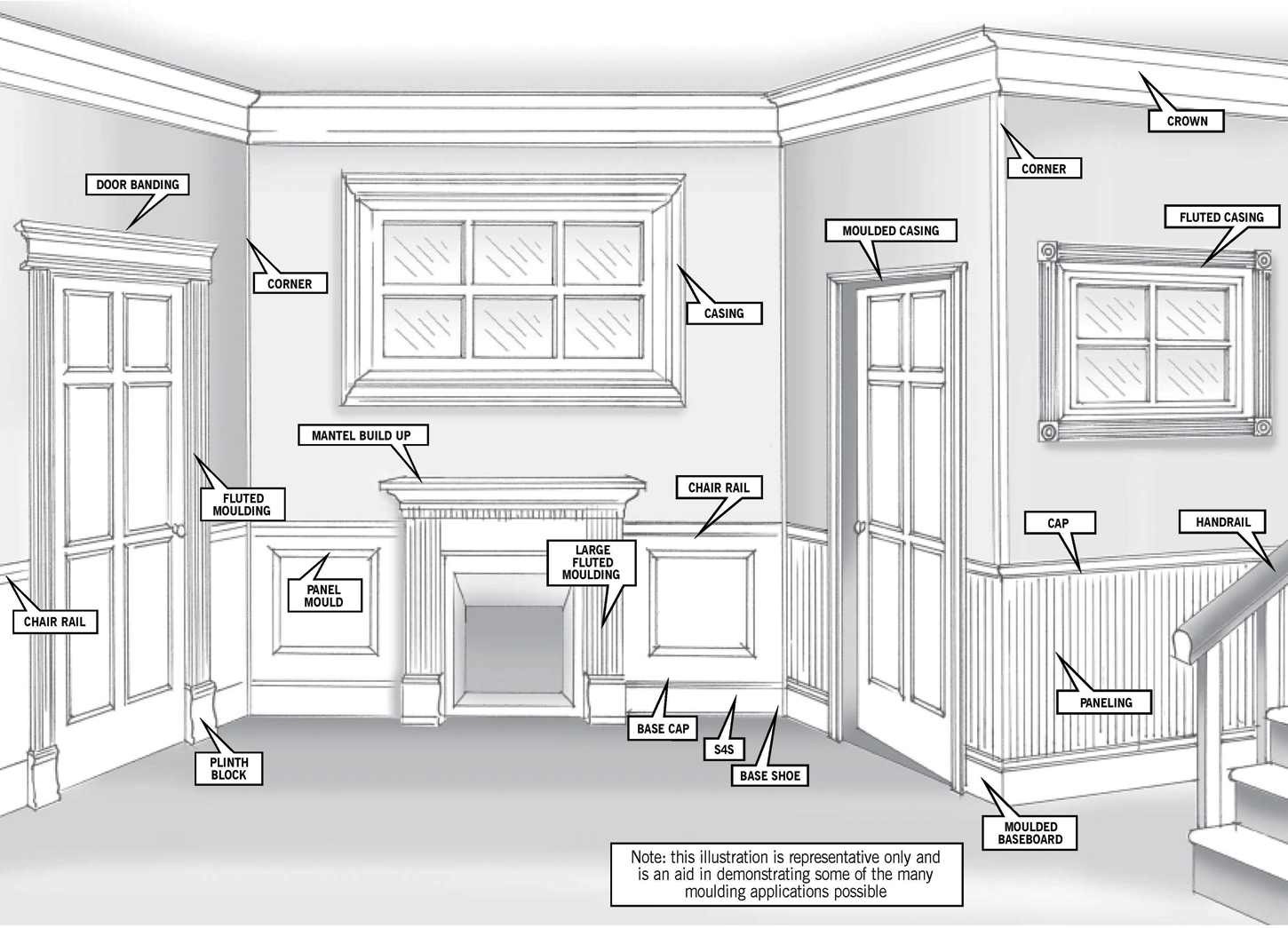
Installing Architectural Moldings. Moldings can be applied with nails, adhesives or both. SpeedFlex 270-5 is an adhesive formulated for architectural application, look here if you need more information. If you are using nails ideally you would like to drive the nails through the molding and into the studs. Nail spacing should be 8 inches apart.
Your Complete Guide to Architectural Moldings · The Wow Decor
plinth. plinth. 1. Plain, continuous projecting surface under the base -moulding of a wall, pedestal, or podium quadra, connecting the architectural member with the ground or floor. 2. In the Classical Orders, the low plain block under the base-mouldings of a column, pedestal, or pilaster. 3. Any monumental support for a statue, etc.

DEG GRC Architectural Moulding, Color Off White at Rs 220 / Running Feet in Alwar DECOR
Definition In classical architecture, the shape of the abacus and its edge profile varies in the different classical orders. In the Greek Doric order, the abacus is a plain square slab without mouldings, supported on an echinus. [2] In the Roman and Renaissance Doric orders, it is crowned by a moulding (known as " crown moulding ").