:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/675/nFGhiyS61hUuKyNtU6cpQ_typical-rib_english.jpg)
Ribs Anatomy, ligaments and clinical notes Kenhub
rib cage, in vertebrate anatomy, basketlike skeletal structure that forms the chest, or thorax, and is made up of the ribs and their corresponding attachments to the sternum (breastbone) and the vertebral column.

Ribs Anatomy,Types,Ossification & Clinical Significance » How To Relief
R i b C a g e Functions The rib cage protects the two major organs in the thoracic cavity, the heart and the lungs. Supports the upper body, keeping it stable. It provides a point of attachment for the clavicles, thus establishing the connection between the arm and the axial skeleton.

Broken Rib Causes, Signs, Symptoms, Recovery Time & Treatment
Last updated: July 14, 2023 Revisions: 42 format_list_bulleted Contents add The ribs are a set of twelve paired bones which form the protective 'cage' of the thorax. They articulate with the vertebral column posteriorly, and terminate anteriorly as cartilage (known as costal cartilage).

anatomy What is the distal portion of the ribs? Medical Sciences
Note the anterior view of the thoracic cage above: The front of the thoracic cage includes seven pairs of vertebrosternal ribs (true ribs), which articulate with the sternum, an elongated flattened bone. There are also three pairs of vertebrochondral ribs (false ribs)—each false rib attaches to the cartilage of the rib directly above it.
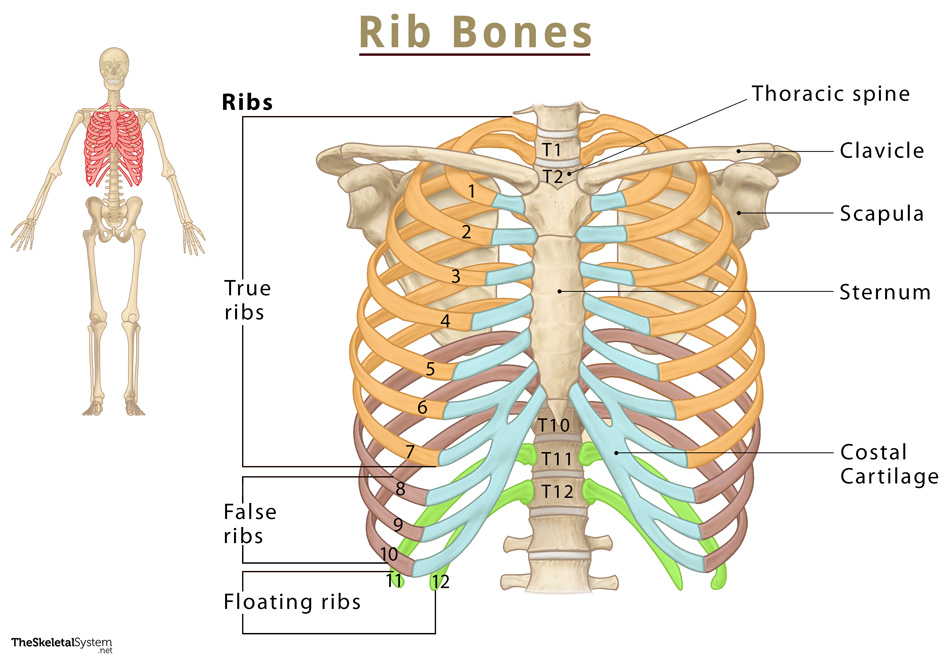
The Ribs Location, Anatomy, Functions, & Labeled Diagram
Media (13) The ribs (Latin: costae) are long, flat and curved bones. They articulate with vertebrae of the thoracic spine forming the majority of the rib cage. The rib cage provides support and protection for such vital internal organs as the heart, lungs, spleen and liver, as well as major blood vessels. Ribs also provide attachment sites for.
Anatomy Of Rib Cage / Ribs Anatomy, Ligaments and Clinical Notes
1 2 Ribs 3-9 share many structural characteristics. In comparison, the first two ribs are shorter and more curved. Rib 1 is also flattened horizontally. The heads of ribs 1, 10, 11, and 12 have a single facet for articulation with the bodies of the thoracic vertebrae.

Diagram Rib Cage With Organs / Anatomy Under Ribs Human Body Anatomy
1/4 Synonyms: 1st-7th ribs, Ossa costalia vera , show more. The ribs are curved, flat bones which form the majority of the thoracic cage. They are extremely light, but highly resilient; contributing to their role in protecting the internal thoracic organs.
Rib Cartilage Injury Masnad Health Clinic
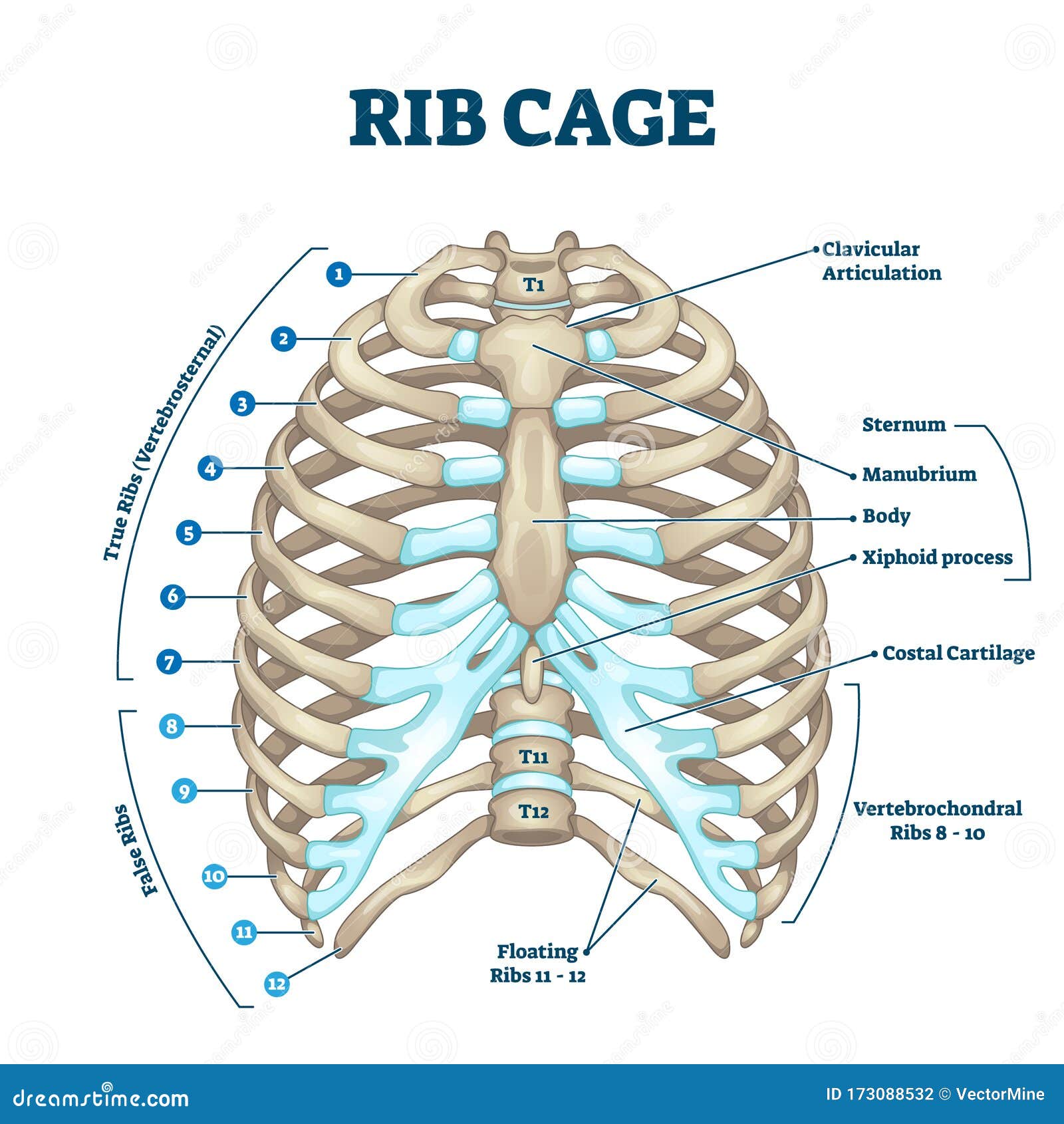
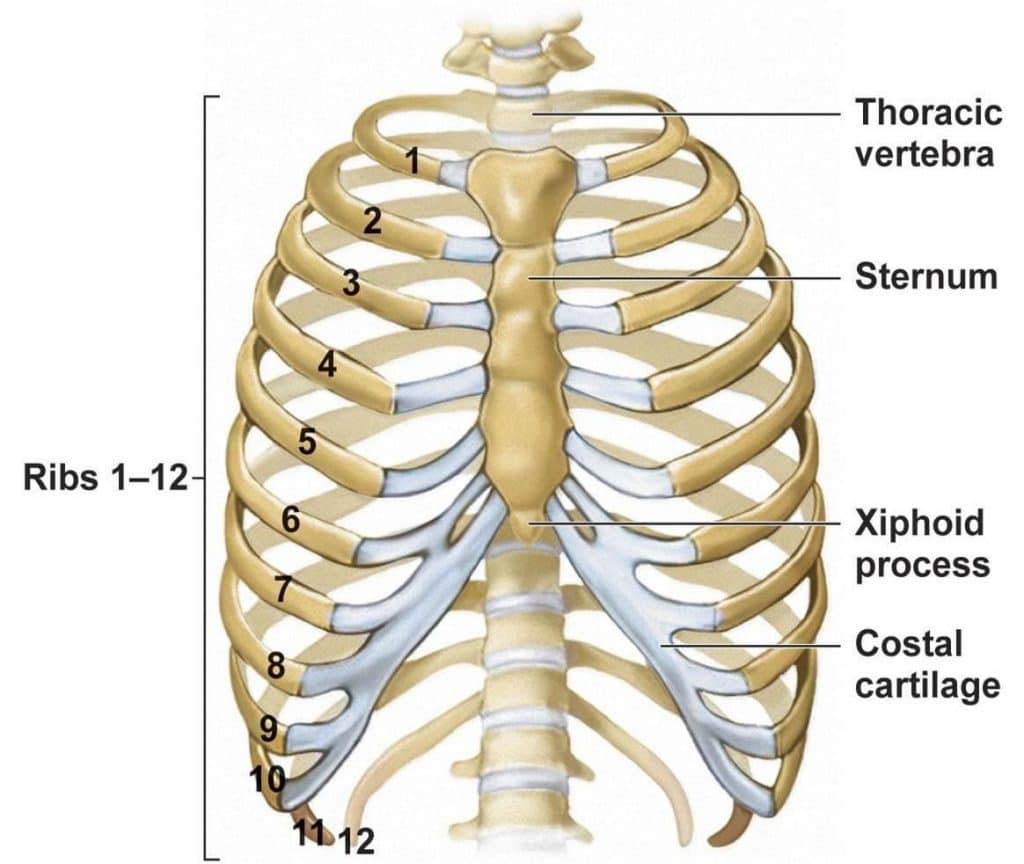
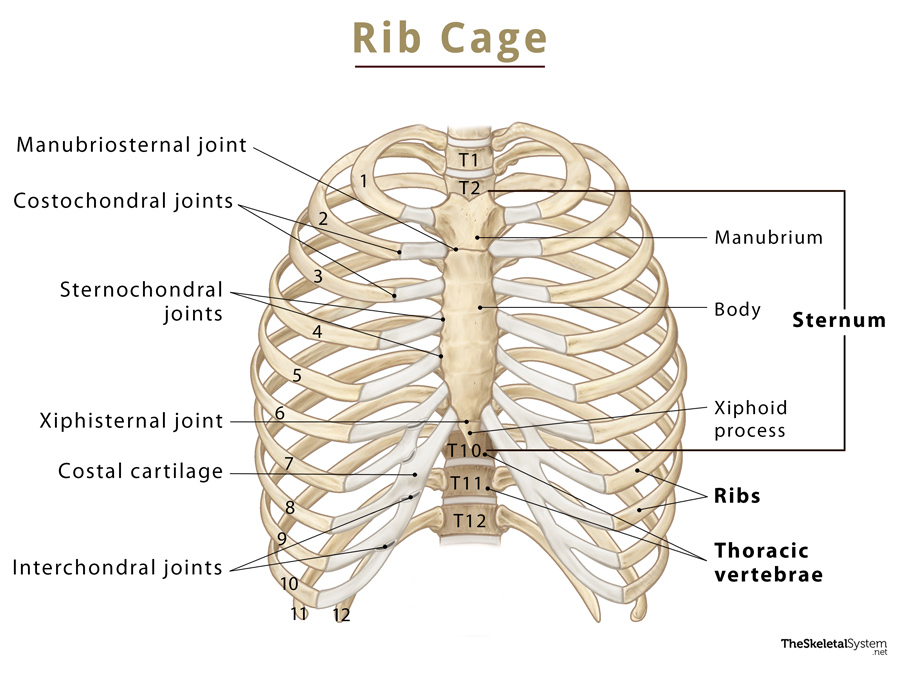
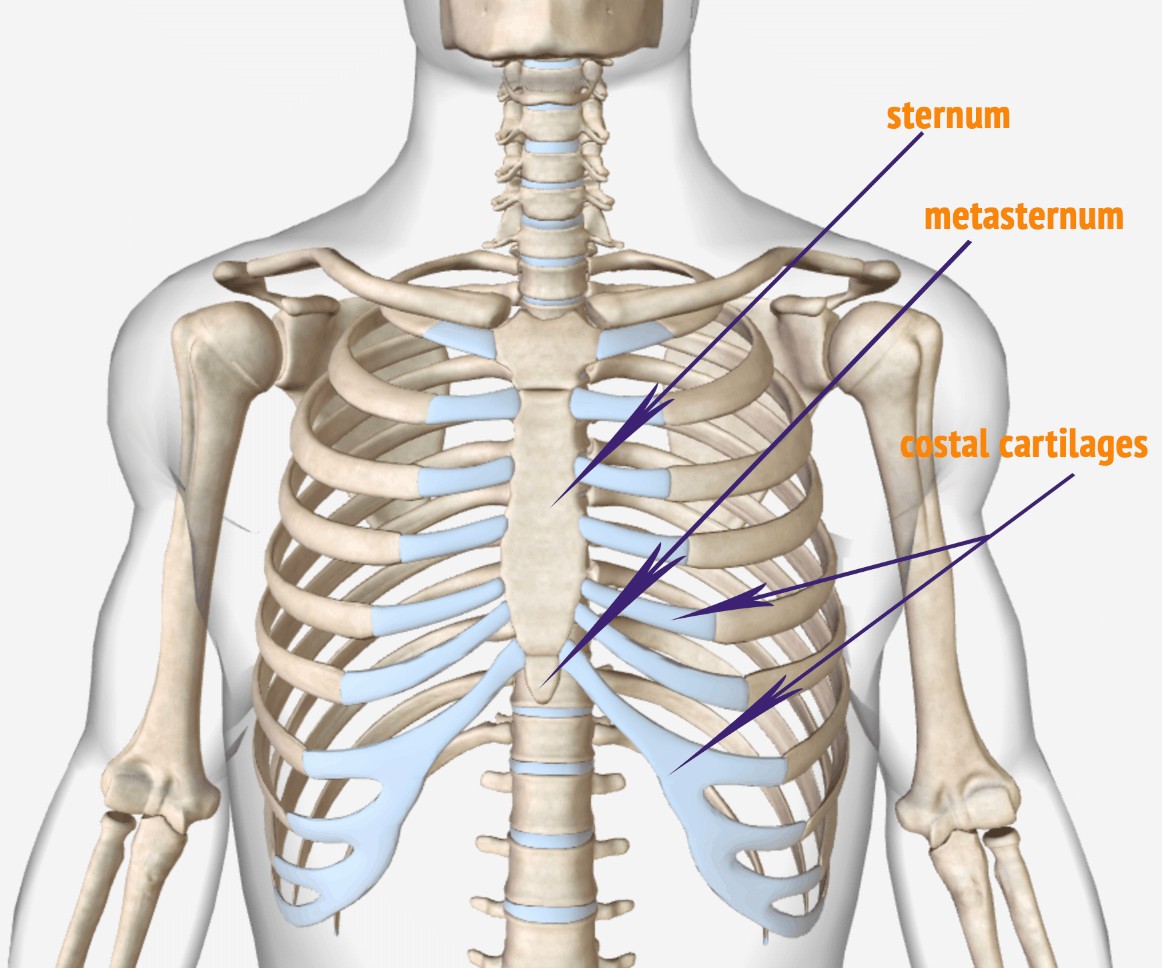
Identify the parts of the sternum and define the sternal angle Discuss the parts of a rib and rib classifications The thoracic cage (rib cage) forms the thorax (chest) portion of the body. It consists of the 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages and the sternum ( Figure 7.32 ).
rib bone 3 anatomy
The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs. Figure 7.5.1 - Thoracic Cage: The thoracic cage is formed by the (a) sternum and (b) 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages. The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae. The sternum consists of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process. The ribs are classified as true.

diagram of human ribs
Human anatomy Rib details. Human ribs are flat bones that form part of the rib cage to help protect internal organs. Humans usually have 24 ribs, in 12 pairs. 1 in 500 people have an extra rib known as a cervical rib.People may have a cervical rib on the right, left or both sides. All are attached at the back to the thoracic vertebrae and are numbered from 1 to 12 according to the vertebrae to.
Rib Cage Names of Bones, Anatomy, Functions, & Labeled Diagram
Parts of a Typical Rib. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) diagrams the bone markings of a typical rib. The posterior end of a typical rib is called the head of the rib.This region articulates primarily with the costal facet located on the body of the same numbered thoracic vertebra and to a lesser degree, with the costal facet located on the body of the next higher vertebra (see Figure 6.4.8: Rib.
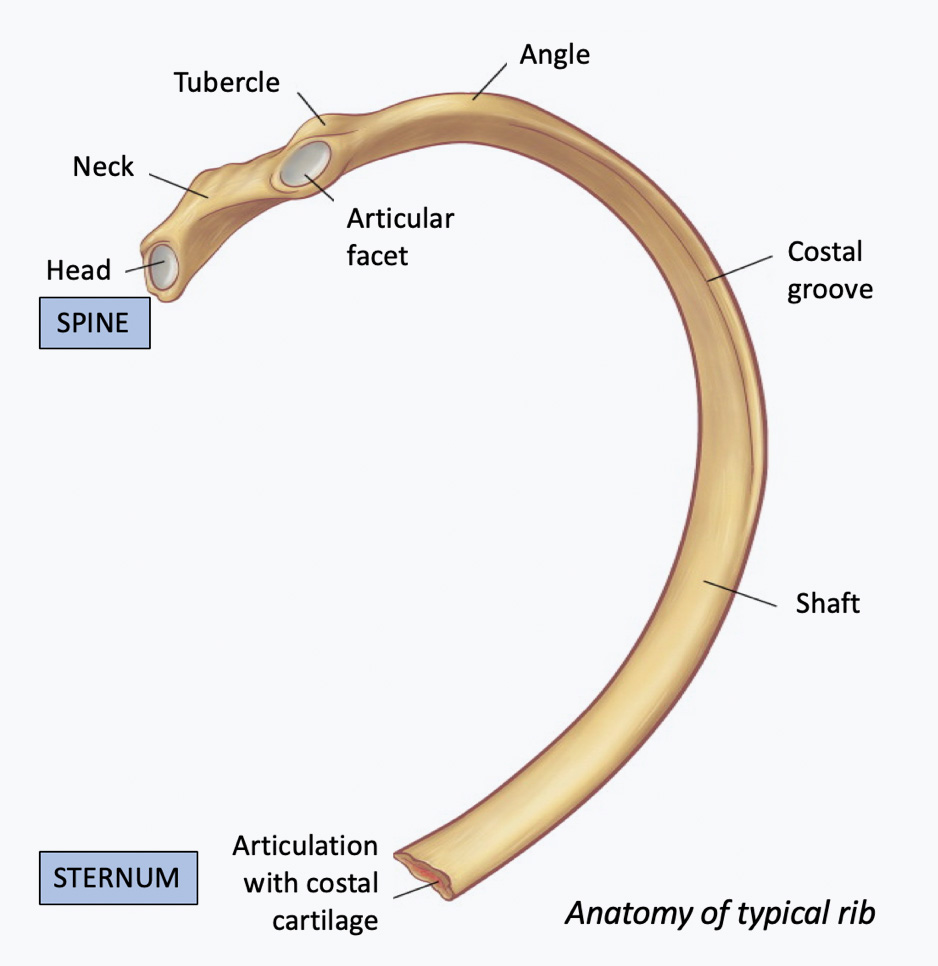
Anatomy Of Ribs Ribs And Sternocostal Joints Rib Characteristics And
Rib Anatomy In this anatomy lesson, I'm going to cover the rib bones, also called costae in Latin. The ribs help protect vital organs in the thorax such as the heart and lungs, and they assist with breathing. Don't be fooled their long, curved shape! Rib bones are not classified as long bones.
Anatomy of The Human Ribs With Full Gallery Pictures
The thoracic cage is a bony case consisting of ribs andsternumwhich encases vital organs like the lungs and the heart and shapes the chest. There are 12 pairs of ribs in the body. They are attached to the vertebral column with most of the ribs anteriorly joining to the sternum bone via costal cartilage.

ribs anatomy labeled
The ribs are the bony framework of the thoracic cavity. Generally, there are twelve pairs of ribs. Each rib articulates posteriorly with two thoracic vertebrae; by the costovertebral joint. An exception to this rule is that the first rib articulates with the first thoracic vertebra only. According to their attachment to the sternum, the ribs are classified into three groups: true, false, and.

Anatomy Of Body What Under Rib Age What Are Neck Ribs Human Yahoo
Anatomy Types of Ribs The 24 ribs are classified in two different ways. There are three types of ribs based on their attachment to the sternum: True ribs are the first 7 pairs that attach to the thoracic vertebra in the spine and then directly articulate with the sternum through their costal cartilage.

rib cage Anatomy & Function Britannica
The thoracic cage, also known as the rib cage, is the osteocartilaginous structure that encloses the thorax. It is formed by the 12 thoracic vertebrae, 12 pairs of ribs and associated costal cartilages and the sternum . The thoracic cage takes the form of a domed bird cage with the horizontal bars formed by ribs and costal cartilages.