Theory Of Wing Sections
Gull wing: sharp dihedral on the wing root section, little or none on the main section, as on the PZL P.11 fighter. Sometimes used to improve visibility forwards and upwards and may be used as the upper wing on a biplane as on the Polikarpov I-153. Inverted gull wing: anhedral on the root section, dihedral on the main section. The opposite of a.

Pilgrim's Chicken Wing Sections 48 Oz Shop Pocahontas IGA
"Most useful in working with wing sections and methods for using section data to predict wing characteristics . . . much detailed geometric and aerodynamic data." -- Mechanical EngineeringThe first edition of this work has been corrected and republished in answer to the continuing demand for a concise compilation of the subsonic aerodynamics characteristics of modern NASA wing sections.

Aircraft Structures
24 Airfoil Geometries Introduction. Aerospace engineers must know how to select or design suitable cross-sectional wing shapes (often called airfoil profiles or airfoils) for use on a diverse range of flight vehicles such as subsonic, transonic, and supersonic airplanes, various types of space launch vehicles, as well as helicopter rotors, propeller blades, wind turbines, UAVs, etc.

Theory Of Wing Sections
The primary reference volume for all the NACA subsonic airfoil studies remains: Abbott, I.H., and von Doenhoff, A.E., Theory of Wing Sections, Dover, 1959. The following paragraphs provide a brief history of the development of the NACA Airfoils. Appendix B provides references to the development of the NASA advanced airfoils, which were.

Theory Of Wing Sections
"Most useful in working with wing sections and methods for using section data to predict wing characteristics . . . much detailed geometric and aerodynamic data." — Mechanical EngineeringThe first edition of this work has been corrected and republished in answer to the continuing demand for a concise compilation of the subsonic aerodynamics characteristics of modern NASA wing sections.

Great Value Buffalo Style Fully Cooked Chicken Wings, 22 Oz lupon.gov.ph
The significance of wing-section characteristics -- Simple two-dimensional flows -- Theory of wing sections of finite thickness -- Theory of thin wing sections -- The effects of viscosity -- Families of wing sections -- Experimental characteristics of wing sections -- High-lift devices -- Effects of compressibility at subsonic speeds.
Theory of Wing Sections of Arbitrary Shape Page 9 of 14 UNT Digital
Overview Streamlines around a NACA 0012 airfoil at moderate angle of attack Lift and drag curves for a typical airfoil. The wings and stabilizers of fixed-wing aircraft, as well as helicopter rotor blades, are built with airfoil-shaped cross sections. Airfoils are also found in propellers, fans, compressors and turbines.Sails are also airfoils, and the underwater surfaces of sailboats, such as.

Theory Of Wing Sections
Airfoils and wing cross-sections. English: This category is for wing cross-sections and airfoils (alt. aerofoils, sometimes called wing profiles ). In a strict sense, an airfoil is the geometry of a wing profile. The word is also used to designate profiles from other wing-like devices (sails, turbine blades, etc).
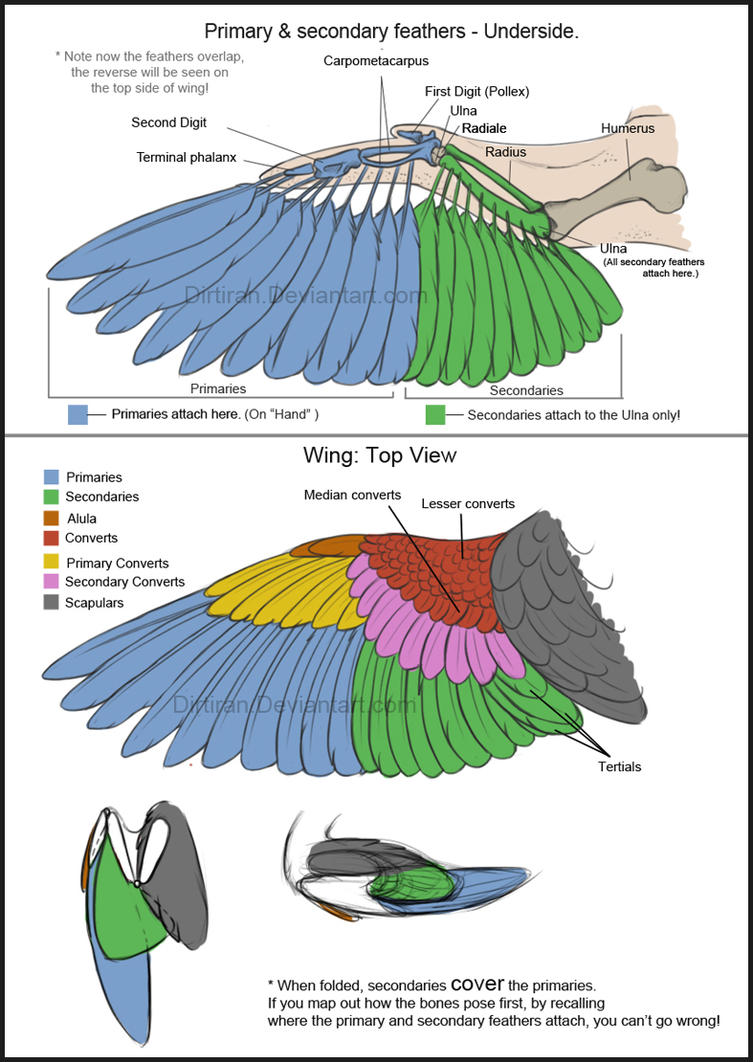
Bird Wings (Tutorial) by KeyFeathers on DeviantArt
"Most useful in working with wing sections and methods for using section data to predict wing characteristics . . . much detailed geometric and aerodynamic data." — Mechanical EngineeringThe first edition of this work has been corrected and republished in answer to the continuing demand for a concise compilation of the subsonic aerodynamics characteristics of modern NASA wing sections.
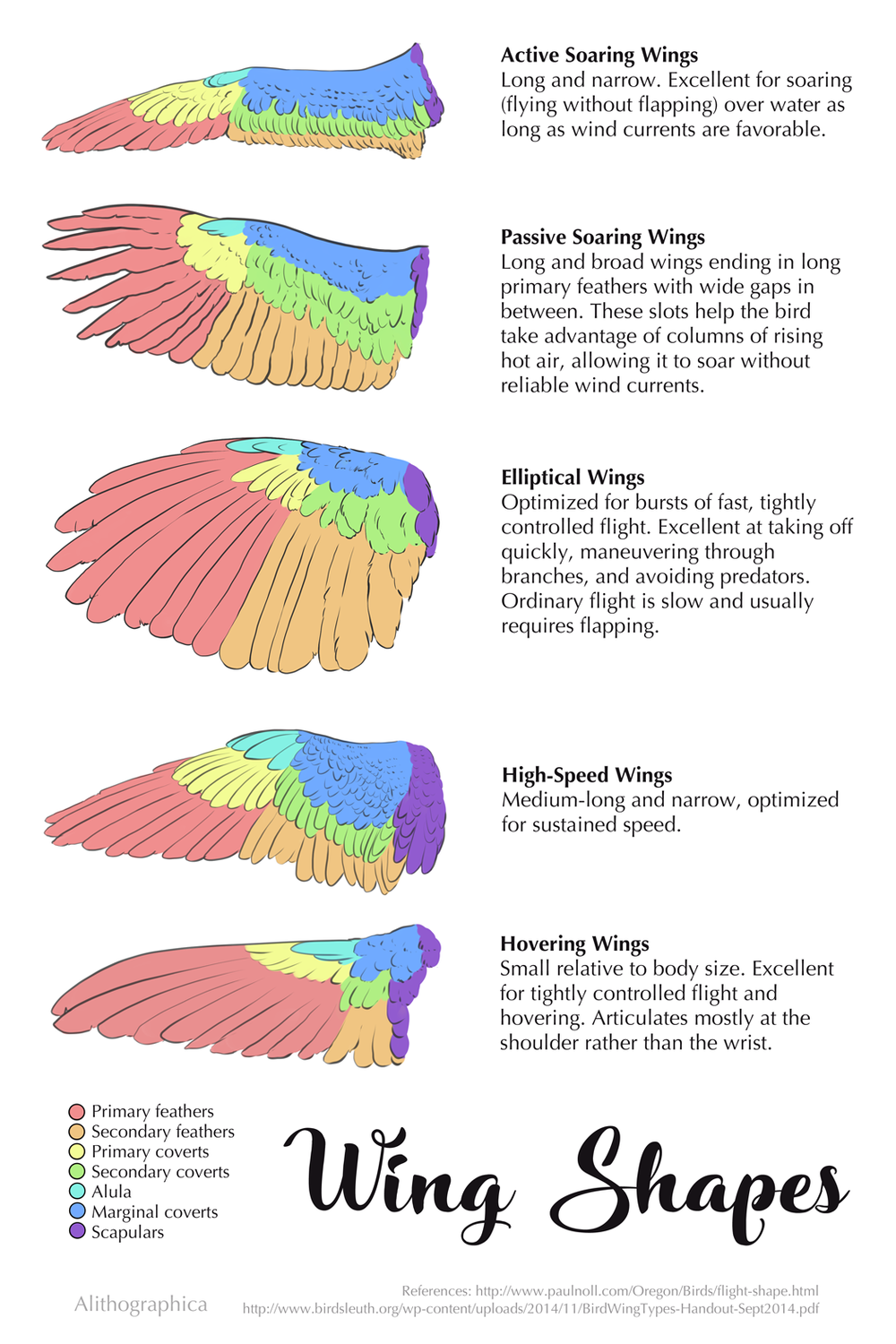
Wing Shapes
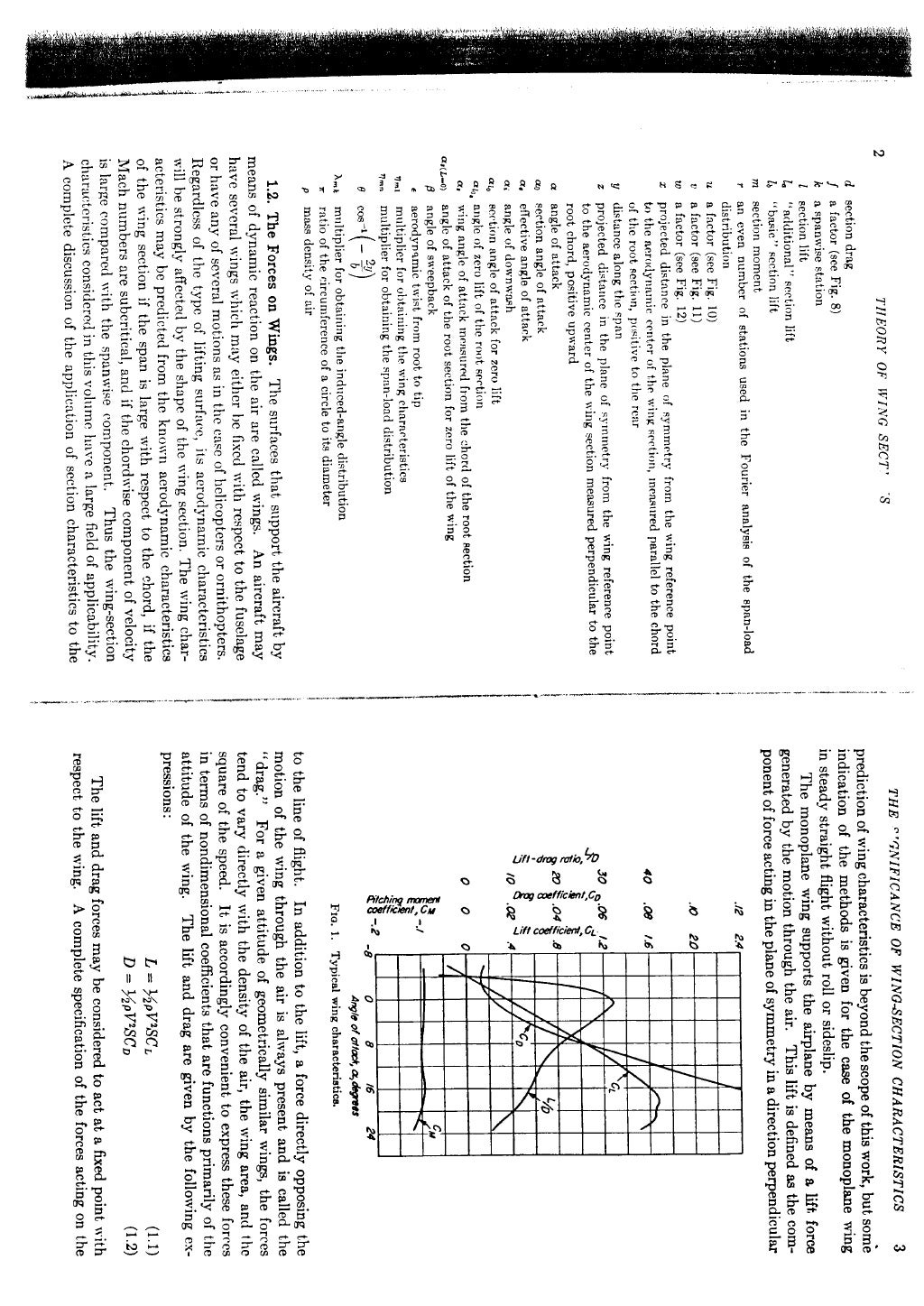
The wing area is a projected area and is almost half of the total surface area. The aspect ratio (AR) of a wing is defined to be the square of the span (s) divided by the wing area (A) . Aspect ratio is a measure of how long and slender a wing is from tip to tip. For a rectangular wing, this reduces to the ratio of the span to the chord length (c):

Great Value All Natural Chicken Wing Sections, 8 lb (Frozen)
Starting with Wing-Section characteristics, the forces on airfoils and their response to those forces are covered in 2D, 3D then fluid analysis. Symbols used in each chapter are identified prior to use. Theoretical treatment is a progression of the developing insight in symbolic approximation from the contributors to understanding aerospace.
Theory Of Wing Sections
Airfoil plotter. View and plot a full size plan of the airfoil to your chord width. The camber, thickness can be adjusted and the pitch set to allow for wing angle of attack, wash out or wind turbine blade angle. The SVG (Scalar Vector Graphics) plan can be printed out full size or over multiple pages for large sections.
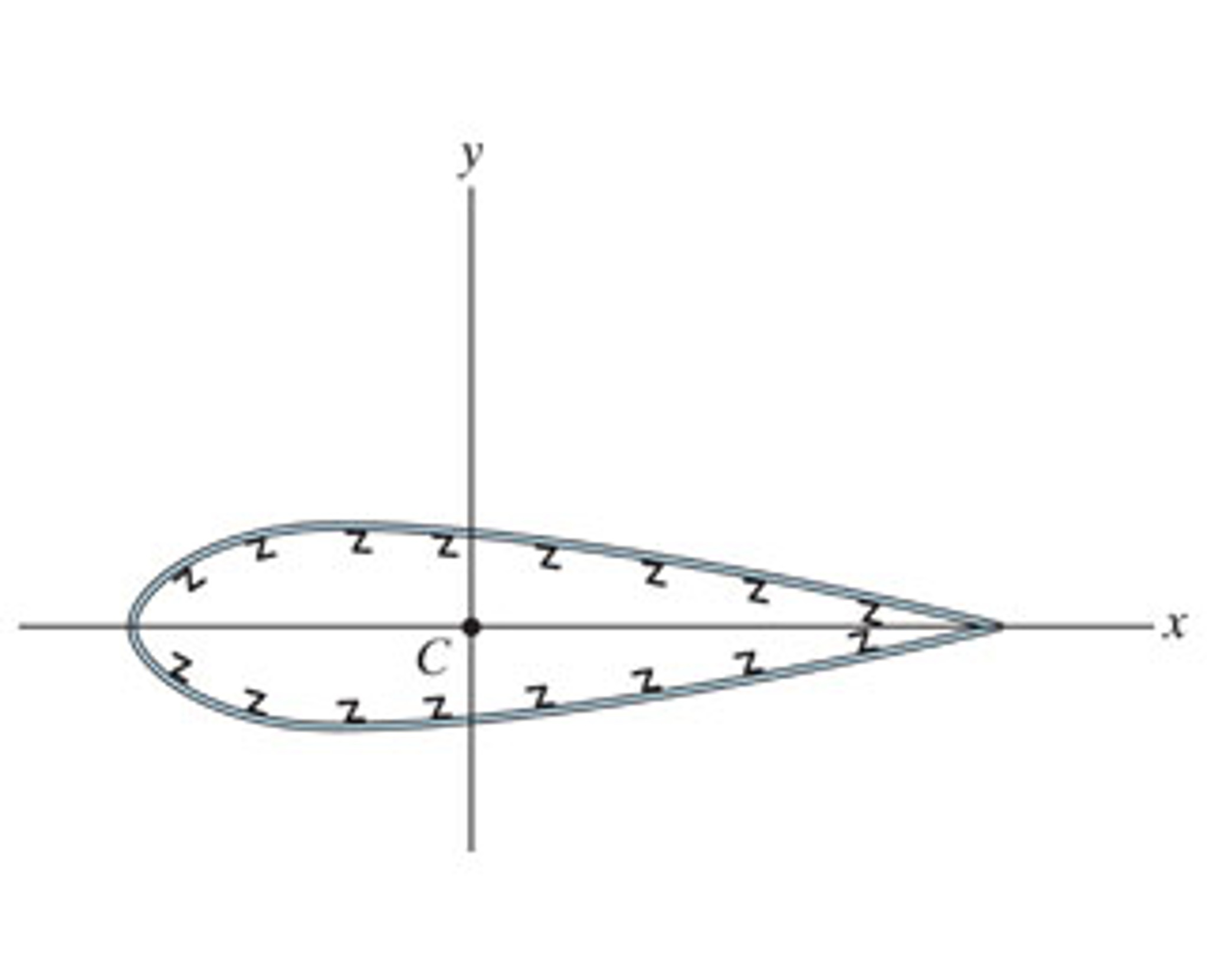
Solved The area of the cross section of an airplane wing has
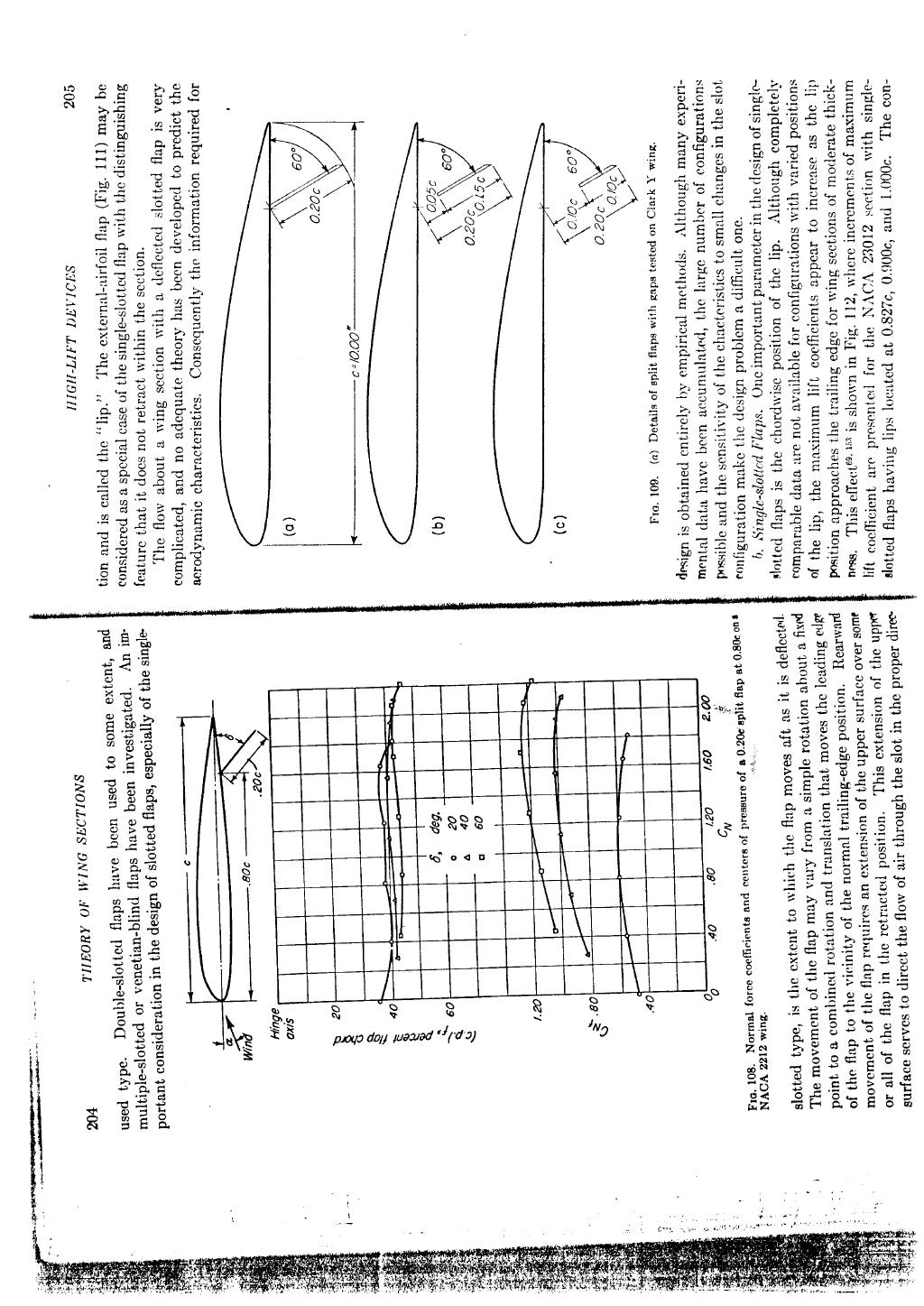
These wing sections are distinguished from the earlier individually derived wing sections by writing the number indicating the Jew-drag range as a subscript, for example, oor 218 a == 0.5 Ordinates for the basic thickness distributions designated by a subscript are slightly different from those for the corresponding individually derived.

Theory of Wing Sections Abbott [PDF Document]
Doenhoff's Theory of Wing Sections, Althaus' and Wortmann's Stuttgarter Profilkatalog, Althaus' Low Reynolds Number Airfoil catalog, or Selig's "Airfoils at Low Speeds". The advantage to this approach is that there is test data available. No surprises, such as a unexpected early stall, are likely. On the other hand, available tools are now.

The Australian LightWing GR LSA Australian LightWing
Airfoil Sections. Wings can use various types and distributions of airfoil sections to suit the application of the aircraft. By cutting a slice out of an airplane wing and viewing it from the side, the wing cross-section is obtained, or what is usually called just the airfoil section or airfoil profile, with an example shown below. It is.

Theory of Wing Sections (eBook) Dover publications, Books, Aeronautics
The wing skins is a semi-monocoque structure are load bearing and carry and transmit shear loads into the neighbouring spar caps and stiffeners. This concludes this post on the wing structural layout. The next post provides a more detailed look at the design and operation of a typical high-lift system.